Business leaders are all too familiar with the pressure of peak demand periods. To meet customer expectations, they know their businesses must operate like a well-orchestrated restaurant kitchen during the lunch rush—with seamless coordination across multiple functions. Yet, unlike that kitchen, where communication happens face to face, departmental teams are often separated by physical distance, different systems, and competing priorities, all of which creates communication gaps that cause delays, errors, and, ultimately, frustrated customers. But by strategically replacing manual processes with automated order processing tools, businesses can eliminate these pain points and strengthen operations across the entire fulfillment cycle from initial customer order to successful delivery.
Whether your business is exploring basic automation to solve immediate bottlenecks or considering a comprehensive system overhaul, automating some or all of the order-to-fulfillment process is likely to deliver tangible operational improvements that can directly increase the bottom line.
What Is Automated Order Processing?
Automated order processing represents a strategic shift from labor-intensive manual order management tasks to technology-driven workflows that require minimal human intervention. These tools replace traditional paper-based or disconnected digital processes with streamlined automation, reducing operational costs while increasing order speed and accuracy.
When a customer places an order, the system initiates the fulfillment process automatically, capturing order details, verifying inventory availability, processing payments, generating picking lists and shipping labels, and updating inventory levels, in real time, to reflect actual remaining stock. Equally as important for growing operations is the fact that many of these systems can scale with the business, handling rising sales volume without incurring proportional increases in staffing or overhead costs.
What Is an Automated Order Processing System?
Think of an automated order processing system as the central nervous system of your order fulfillment operations. Rather than forcing employees to manually bridge the gaps between siloed systems, these solutions integrate with existing infrastructure to connect customer-facing platforms with back-end inventory management tools, eliminating the redundancies and inefficient communications that slow fulfillment and frustrate customers. This operational hub coordinates multiple components, including ecommerce platforms, warehouse management systems, shipping software, compliance features, and accounting programs, to create a unified workflow that progresses from order placement through delivery.
More advanced automated order processing systems incorporate additional technologies, such as barcode scanners, radio frequency identification readers, robotic picking, and analytics enhanced with embedded artificial intelligence capabilities. These forward-thinking advances create a resilient operation that can adapt more rapidly to changing market demands.
Key Takeaways
- Automated order processing systems eliminate manual tasks and reduce errors throughout the fulfillment process, ranging from customer order through delivery—and returns.
- Modern automation tools provide real-time visibility across departments, giving businesses and customers relevant insights into key metrics, such as inventory availability, order status, and delivery timing.
- Advanced features, such as automated inventory updates, robotic warehouse tools, carrier selection, and label and document generation, help businesses cut down on overall processing time and costs.
Automated Order Processing Explained
For businesses coping with shifting markets and evolving customer expectations, modern order processing systems offer adaptive intelligence and flexible frameworks to help your business adapt. Instead of perpetuating rigid workflows, today’s automated order processing tools can flex with changing business rules and customer requirements, enabling businesses to implement new order processes or special handling rules without extensive IT involvement or system overhauls.
Automated order processing systems also can become part of an early warning system that analyzes order patterns to inform inventory planning, staffing decisions, and growth strategies. They can flag potential issues before they affect customers, giving your team the ability to solve the problem rather than having to hunt to find essential data. And for businesses with facilities in multiple locations, these systems can intelligently route orders based on such factors as inventory availability, warehouse proximity to the customer, and promised delivery timelines— simultaneously optimizing both cost and customer experience. This intelligence extends across departmental boundaries to connect fulfillment operations with vendor and warehouse management and procurement. For example, when inventory approaches predetermined thresholds set by the business, the system can automatically place reorders with appropriate suppliers, preventing stockouts and emergency “expedites” that erode profit margins and strain vendor relationships.
Automated vs. Regular Order Processing
Manual, or “regular,” order processing requires staff attention at every stage—to enter orders, update inventory, pick, pack, ship the order, and notify the customer. Automated systems, of course, can be configured to do all this with little, if any, human intervention.
But the usefulness of automated ordering systems really shines when customers modify their orders. Whereas manual processes require staff to chase updates across multiple departments and systems, automated order processors can instantly propagate the changes to all affected systems. This single capability not only prevents costly shipping mistakes and returns, but fundamentally changes how employees spend their time—shifting from administrative coordination to higher-value customer service and process improvement activities.
How Does Automated Order Processing Work?
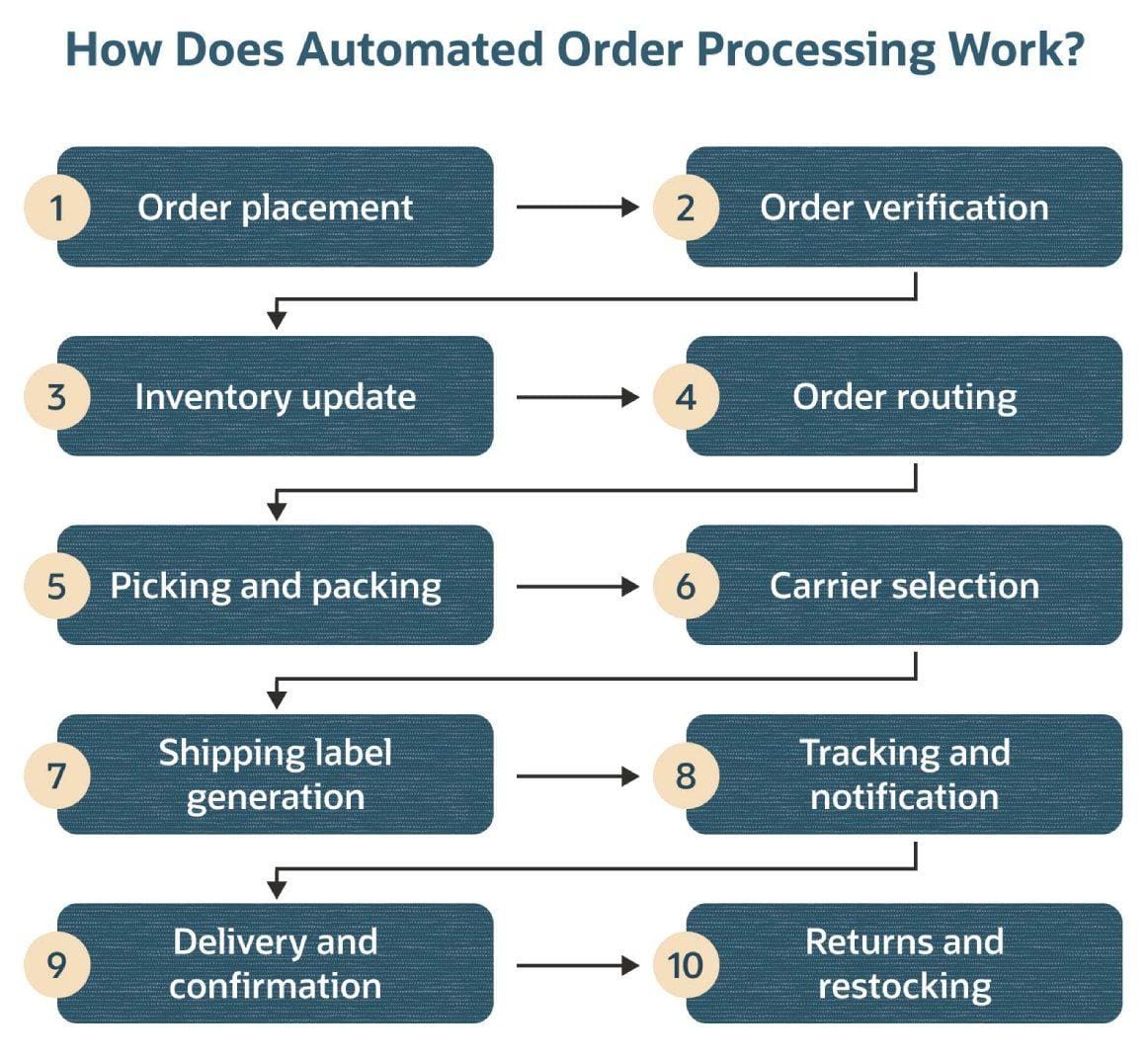
Automated order processing systems perform a series of interconnected steps. Each step automatically propels the order to the next step, increasing accuracy, shortening processing time, and maintaining real-time communication between systems and relevant staff as the process moves along. Here’s how an automated order processing system typically works.
- Order placement: When customers place orders through any channel, the system captures all details without manual intervention, virtually eliminating the data entry errors that frustrate both your team and customers.
- Order verification: Before order fulfillment begins, the system checks for fraud, verifies stock availability, and confirms payment information—reducing the fire drills teams face when these issues are discovered mid-fulfillment. At this point, the customer is usually notified that the order is in progress.
- Inventory update: The system identifies the specific items for the order and their locations. It then allocates the items to the order, updating the available inventory to reflect that these items are now reserved. Stock levels automatically adjust in real time across all connected systems and warehouse locations, triggering reorder alerts or reallocation when inventory reaches predetermined thresholds.
- Order routing: Based on factors, such as available inventory and the customer’s location and delivery requirements, the system sends the order to the warehouse or fulfillment center that will minimize shipping time and/or costs.
- Picking and packing: The warehouse team receives the order details along with optimized picking instructions that include precise item locations and the most efficient routes through the warehouse to collect them. Advanced operations equip pickers with barcode scanners and other mobile tools, or may even send the instructions to robot pickers.
- Carrier selection: The system analyzes all available and preferred shipping options to select the carrier that best meets cost and service requirements for each order. Beyond cost, it examines route optimization, delivery speed requirements, and any specific business or customer preferences.
- Shipping label generation: Fulfillment teams use the system to automatically generate shipping labels with all necessary documentation, including invoices, customs forms, tracking numbers, and any other relevant information.
- Tracking and notifications: Both customers and the customer service team receive automated updates about order status and delivery progress, in real time, stating whether there are any unforeseen changes, such as inclement weather or carrier problems. This averts “Where is my order?” inquiries, allowing the team to focus on higher-value customer interactions.
- Delivery and confirmation: After the carrier delivers the package, the system notifies all parties that the order is complete. It can potentially trigger personalized follow-up communications, such as product guidelines, return policies, how to reorder, or opportunities to give feedback, that serve to strengthen customer relationships and encourage repeat business.
- Returns and restocking: Should returns be necessary, the system can guide the process from authorization to restocking and can provide data that helps the business identify and address product or process issues. In addition, it can automatically update inventory levels when restocking products to maintain accurate inventory records for when the cycle begins again.
Benefits of Automated Order Processing
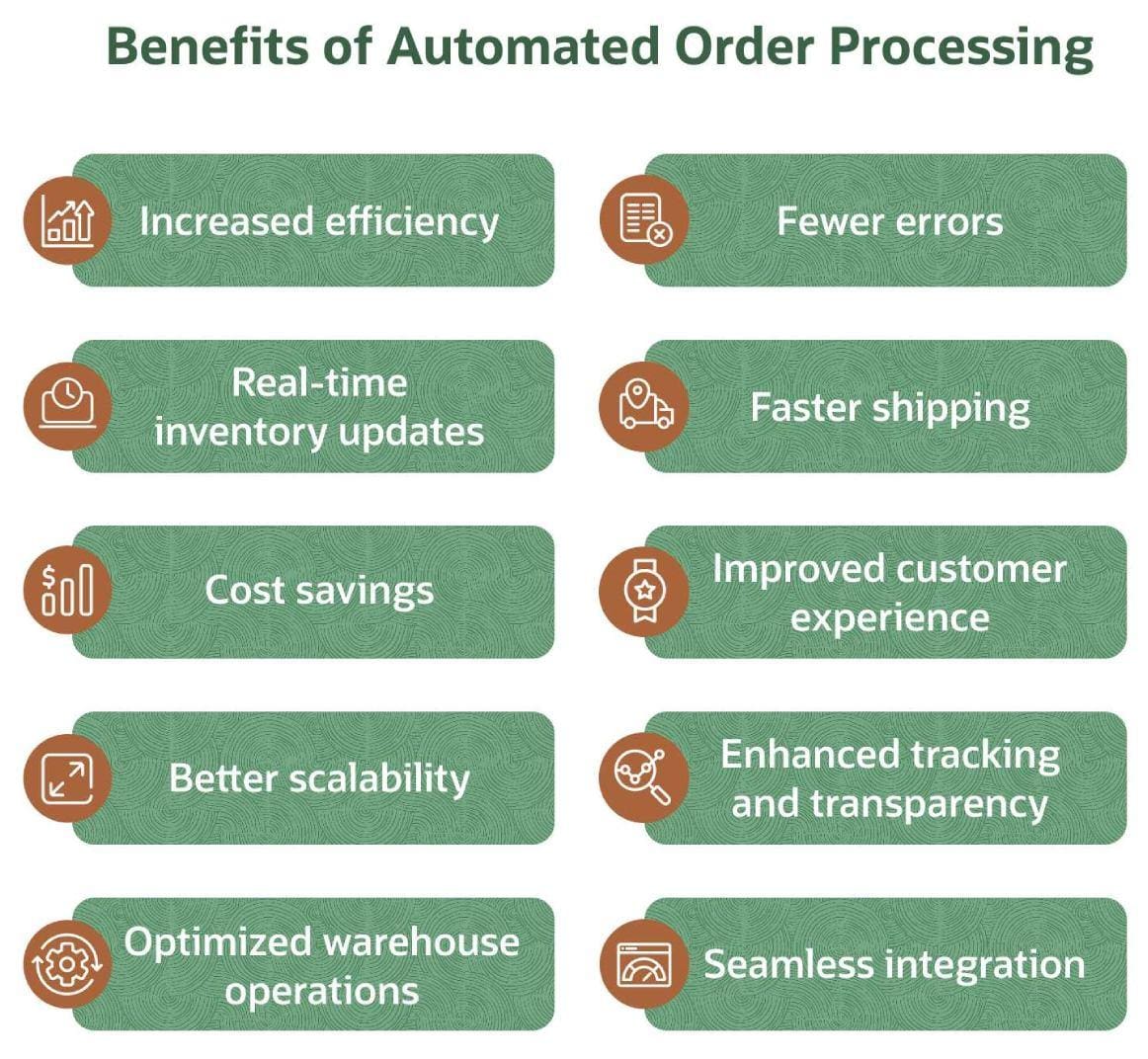
Implementing automated order processing delivers both immediate operational improvements and long-term strategic advantages. Here are the key benefits you can expect to see.
- Increased efficiency: Automated systems simplify workflows and eliminate manual tasks at each fulfillment stage, such as document generation and order routing. This means being able to handle more orders without proportional head-count expansion—in other words, you boost productivity and output speed.
- Fewer errors: By removing manual data entry at multiple points, you will see an immediate reduction in costly mistakes, such as incorrect shipping addresses, wrong item selection, or quantity errors. This translates into fewer returns, less rework, and higher customer satisfaction scores.
- Real-time inventory updates: Order processing systems maintain appropriate stock levels at all locations because they automatically update inventory counts as orders are placed, processed, and fulfilled. This real-time visibility facilitates more confident purchase decisions, helping businesses to prevent stockouts and improve demand forecasting.
- Faster shipping: Intelligent carrier selection and route optimization help companies decrease both processing time and transit time, which are crucial considerations for perishable or other time-sensitive deliveries. And because customers’ delivery speed expectations continue to accelerate, this benefit can directly improve customer retention and satisfaction.
- Cost savings: Automated order processing systems help business leaders identify and implement cost savings opportunities throughout the fulfillment process, including quicker intake for customers and more cost-effective picking methods. These systems also generate the data companies need to negotiate more favorable terms with suppliers and shipping partners. Individually, these may seem to be merely incremental improvements, but they can compound—across the entire fulfillment process and over time—and add up to a significant bottom-line impact.
- Improved customer experience: Accurate orders, real-time tracking, and reliable delivery windows help businesses deliver on their fulfillment promises consistently—another benefit that can increase customer retention and lifetime value. Meanwhile, service teams with instant access to customer order status and histories can resolve issues faster and with a more personalized touch.
- Better scalability: Businesses can rely on automated systems to handle increased order volume and speed without requiring proportional increases in staff or resources. This scalability allows companies to manage seasonal peaks, promotional periods, and long-term growth without the traditional staffing challenges—and costs—these fluctuations create.
- Enhanced tracking and transparency: Real-time visibility into order status, inventory levels, shipping progress, and any other operational key performance metrics enable more informed strategic planning. This transparency extends across departments, breaking down the silos that often exist among sales, operations, and customer service teams and fostering more open communication.
- Optimized warehouse operations: Automated picking instructions, better floor plans, and strategic inventory placement help businesses limit picking errors and minimize warehouse walking time, all of which nets down to more accurate orders, delivered faster. These benefits help companies maximize the productivity of their facilities and optimize warehouse operations.
- Seamless integration: The right order processing system for a business should seamlessly connect with existing software, including ecommerce platforms, customer relationship management (CRM) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, accounting software, and third-party systems, such as those preferred by your shipping carriers. This integration can go a long way toward eliminating the fragmented workflows and communication breakdowns that can occur among such systems, as well as creating a unified operational environment.
Automated Order Processing Examples
Just about any business that manually processes orders can hone its operational efficiency and customer satisfaction by implementing automation. The following solutions range from targeted tools that address only a single pain point to comprehensive enterprisewide systems. Here are some strategic applications that businesses are implementing.
- Order management systems (OMSs) are among the comprehensive solutions. They process and track orders from receipt to delivery—and beyond, if the company offers returns, exchanges, or post-purchase services. For example, when a clothing retailer receives orders for the same jacket through its mobile app and physical store, the OMS coordinates fulfillment and updates inventory counts across both channels, and tracks and processes any returns.
- Barcode scanning lets businesses accurately identify products as they move through picking and packing on their way to shipment. An electronics distributor’s warehouse staff, for instance, can use handheld scanners to verify model and serial numbers for computer components, minimizing return rates that would erode margins and damage customer relationships.
- Automated inventory updates have the potential to elevate supply chain resilience. They track stock levels across all locations and sales channels in real time, and can generate the data necessary to intelligently rebalance inventory across facilities and trigger replenishment orders, helping the company maintain service levels without holding excessive safety stock. Say a food distributor’s Chicago warehouse runs low on a popular item. Its system can automatically reroute incoming orders from its Milwaukee facility to Chicago and then trigger a restock order from its supplier to replace the diverted goods.
- Shipping label generation allows delivery teams to create and print shipping documentation based on exact order details and carrier requirements. A cosmetics company’s system, for example, might automatically generate five-day shipping labels for standard orders but upgrade time-sensitive or high-value orders to overnight shipping. In an ecommerce environment, it could offer customers that option at an additional cost.
- Order confirmation emails or texts build customer confidence without burdening your team. An office supply company might automatically send customers text messages when their order is picked, another when it ships, and a follow-up survey alongside the final delivery confirmation. These communications deter support inquiries and create opportunities for additional customer engagement.
- Carrier rate integration automatically calculates and compares the shipping costs of multiple carriers in real time to find the most cost-effective option—and it can optimize for both cost and service level based on the business’s strategic priorities. When shipping furniture, for instance, a seller’s system would consider dimensions and weight, delivery zones, and special handling requirements or service levels (assembly, taking away the old item, etc.).
- Warehouse robotics bolsters the picking and packing process through autonomous equipment that transports items from storage to shipment preparation. An automotive parts distributor with thousands of small components may use robotic picking systems to retrieve items from high shelves, reducing worker fatigue and accidents while better utilizing the entirety of the warehouse’s space.
- Fraud detection tools automatically screen orders for suspicious patterns or incorrect information before processing begins. Many ecommerce systems flag potentially fraudulent transactions by detecting customer information mismatches, unusual order quantities, or suspicious payment methods to prevent chargebacks and help ensure that legitimate customers experience no friction.
- Returns processing automation has the potential to transform a cost center into a competitive advantage. Your team can create a seamless returns experience that builds customer loyalty while minimizing the operational impact through automated tracking, inventory updates, and refund processing. This not only pares the costs associated with restocking and return shipping— including customer-service labor costs—but opens new opportunities. For online clothing shoppers who will be trying on clothes for the first time at home, many ecommerce retailers use these systems to automatically generate return labels, track incoming packages, update inventory counts when items are received, and process customer refunds.
- AI-powered demand forecasting can help a business predict future inventory needs based on historical sales data and market trends. A sporting goods manufacturer, for example, can use AI capabilities in demand forecasting to analyze past order patterns, seasonal fluctuations, and the effects of promotions to inform stock purchase decisions, potentially reducing both stockouts and excess inventory.
Future of Automated Order Processing
In the near term, expect automated order processing systems to become more capable and accessible to businesses of all sizes that are seeking operational excellence. In particular, AI advancements, which are enhancing these systems’ ability to predict issues, automate increasingly complex operations, and recommend more accurate and targeted decisions, appear to be shifting executive decision-makers’ mindset from defensive to offensive.
According to the 2025 AlixPartners Disruption Index, 80% of 3,200 executives surveyed view AI optimistically, with 61% prioritizing revenue growth use cases (and only 39% focused specifically on cost reduction). To accomplish this, companies are expected to start deploying AI into demand forecasting and inventory management that will go beyond extrapolating from historical data to analyze subtle patterns in customer behavior and market dynamics that human analysts might miss. This enhanced visibility will equip leadership teams to make more confident inventory decisions and capital allocations.
Perhaps the most vital competitive advantage to emerge from modern order processing systems, however, will come from breaking down remaining organizational silos that fragment customer experiences. Not only will these systems connect an ever-wider range of internal business systems, but they will integrate with external partners, too—vendors, manufacturers, logistics partners, and delivery networks. Combining this with additional foresight from AI deployments may transform the way organizations respond to supply chain disruption, shifting them from reactive damage control to proactive scenario planning.
For internal operations, advanced robotics also is expected to become more widespread and accessible, complementing human workforces in new ways. These systems can now safely handle delicate items, manage complex sorting operations, and adapt their behavior to changing conditions, helping organizations to maintain consistent performance during demand spikes or labor shortages. According to the AlixPartners survey, 72% of executives foresee deployment of humanoid robots occurring, at scale, within the next five years, suggesting a fundamental rethinking of workforce composition.
These and other technological advances are making automated order processing more intelligent and flexible, letting businesses handle increasingly complex fulfillment challenges while maintaining their competitive edge. Organizations that view automated order processing merely as an operational improvement, rather than as a strategic imperative, may find themselves at a disadvantage as customer expectations evolve.
Automate Order Processing With NetSuite
When a company prioritizes order processing, the benefits often reverberate throughout the organization, resulting in a strengthened bottom line and more satisfied customers and employees. NetSuite’s order management software directly addresses order processing challenges by automating key fulfillment steps, such as order intake, product picking, order routing, and multilocation inventory tracking. With NetSuite, companies can set custom rules throughout the ordering process, including unique pricing strategies for individual sales channels or specific steps for refunding or exchanging returned goods. And NetSuite’s built-in advanced analytics tools with embedded AI capabilities help business leaders identify potential issues early, which can create a cycle of iterative improvements in how the business delivers for its customers.
Because NetSuite automated order processing is part of the company’s unified cloud-based ERP system, it seamlessly integrates with financial management, inventory control, and CRM modules to provide a comprehensive picture of the business’s customer fulfillment operations. This integration enables real-time visibility across the entire order-to-cash cycle, allowing companies to find areas where they can reduce costs, improve cash flow, and enhance the customer experience. By integrating order processing into other critical business functions, NetSuite gives business leaders a scalable solution that adapts to their needs and to those of their evolving customer base.
NetSuite Automates the Entire Order Management Process
Automated order processing can significantly boost a business’s operational efficiency and customer satisfaction while reducing its costs. With the right combination of tools and technology, companies can eliminate manual tasks, errors, and workflow weaknesses at every step between initial order placement and final delivery or product return. Companies that leverage order processing automation—whether by automating individual tasks or deploying a comprehensive order processing system—create a more agile and competitive company that will be better able to serve customers and scale operations as it grows.
Automated Order Processing FAQs
How can businesses improve order processing?
To improve order processing, start by identifying the primary bottlenecks and inefficiencies in fulfillment steps. Then implement automation tools that directly respond to those specific challenges. If address labels have a high error rate, for example, automate customer intake and shipping label generation. Start with one or two processes with high return potential, measure the impact, and then expand efforts to other areas.
How long does order processing take?
Order processing time varies significantly with order complexity, product type, and current workflows. Manual processing can be slow; automated systems can significantly shorten processing time and speed up the order-to-cash cycle. However, more complex orders may still require additional time for special handling or verification steps, especially if they involve customization.









