Telecommunications providers are at the center of converging pressures. Customers expect quick activation for increasingly complex services. At the same time, new technologies have intensified competition and introduced intricate configurations that telecom providers may struggle to manage with legacy systems. Ineffective order management, exacerbated by the inclusion of manual processes, means that as sales volumes grow, orders can fall through the cracks. The result? Costly delays that start customer relationships off on the wrong foot.
Digital order management systems help telecom companies automate order fulfillment processes to accelerate service delivery and improve customer satisfaction. This guide explores the core processes involved, the benefits and challenges telecom providers can expect, and the enterprise platforms that underpin effective telecom order management.
What Is Telecommunications Order Management?
Telecommunications order management is the end-to-end process that tracks and executes each step of a service order from initial request through service activation and billing. It includes validating orders, coordinating workflows, scheduling services, and addressing exceptions for systems and departments—accurately and consistently.
Telecom companies increasingly use a centralized telecom order management system to connect data derived from customer-facing channels with data from network operations, billing systems, and field service teams. By integrating data and systems, companies can automate complex workflows—managing service dependencies, allocating network resources, and coordinating efforts throughout the service lifecycle—to accelerate service delivery, reduce costs, and boost customer satisfaction.
Key Takeaways
- Telecommunications order management systems automate the steps involved in a service order from initial request through billing.
- Digital order management can prevent billing errors, improve customer satisfaction, and accelerate revenue recognition.
- Comprehensive telecom order management processes should address common challenges, including complex service configurations and order fallout.
- Enterprise platforms and AI can automate complex order management workflows, provide real-time tracking, and support continuous improvements.
Telecom Order Management Explained
Telecom order management is evolving from its start as a back-office process into a critical driver of revenue and customer experience. It makes sense: As telecom services have become more commoditized, providers are finding it harder to raise prices, even as customer expectations climb. A PwC report projects US mobile subscribers to grow 4.9% annually through 2028, but average revenue per user to decline 1.5%. And according to Simon-Kucher’s “2025 Global Telecommunications” study, telecom companies are capturing only 60% of their total customer-value potential, despite the fact that retaining customers costs 10 times less than acquiring new ones.
By prioritizing order management, telecom companies can begin to shrink the revenue and value gap. Faster activations and consistent experiences strengthen retention rates and improve their bottom lines. Behind the scenes, every customer order—whether for a basic broadband connection, a new mobile plan, or an intricate enterprise network deployment—requires coordinating multiple systems, teams, and tasks, including allocating equipment, scheduling technicians, configuring networks, and setting up billing. These steps span both physical fulfillment (for example, shipping routers, modems, or set-top boxes) and digital provisioning (for example, assigning bandwidth, IP addresses, or security credentials).
When these workflows are executed accurately and in sync, telecom companies see measurable gains in key performance indicators (KPIs), such as order cycle time, first-call resolution, and revenue per customer. High-performing providers can launch services faster, customize bundles to suit their customers’ needs, and respond quickly to meet new market demands.
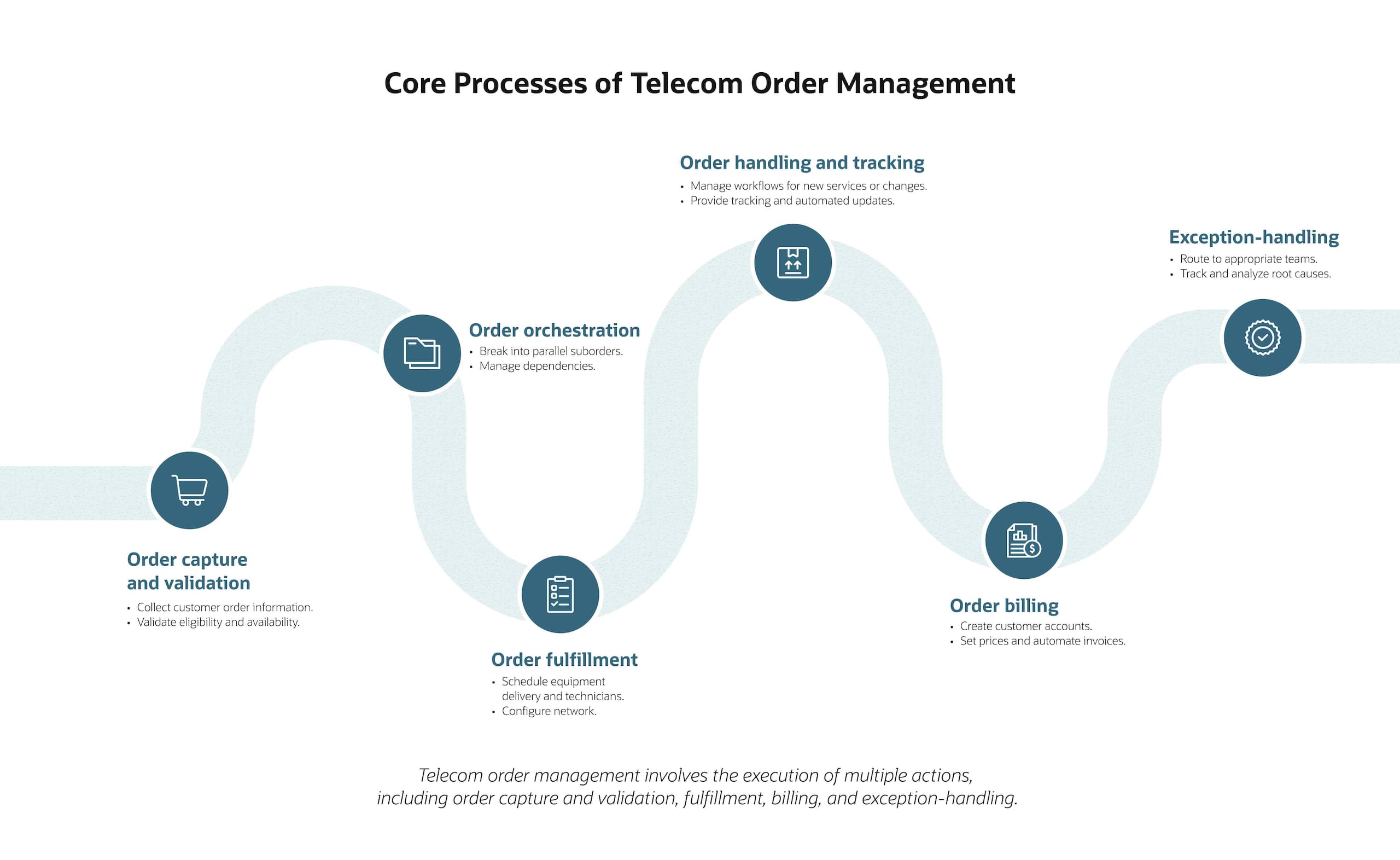
Core Processes of Telecom Order Management
Telecom order management consists of six interconnected processes, starting with a customer request and ending with billing or exception-handling. Proactive monitoring at each stage helps teams detect and resolve issues before they can disrupt operations or impact the customer experience:
- Order capture and validation: The first phase of order management is capturing information from multiple channels (such as ecommerce sites, mobile apps, brick-and-mortar retail, and partners), then assessing customer eligibility, service availability, and technical feasibility for each order. Businesses should validate this data before fulfillment begins to address any issues proactively to reduce downstream impacts, such as higher return rates or wasted resources.
- Order orchestration: Next, a telecom provider will break orders into actionable steps, each tracked and—when possible—executed in parallel to minimize delays. For example, a triple-play order for broadband, TV, and voice services would be split into three activations, each processed according to its own technical and resource requirements.
- Order fulfillment: The third phase of order management involves marshaling the physical and digital efforts required to fulfill the order, including shipping equipment, dispatching technicians, and configuring networks. Coordinating these activities helps the telecom business deliver assets by promised delivery dates. For example, a cable box would be delivered to a customer’s house or a technician’s station before the scheduled service window so the technician can complete the work in one visit.
- Order handling and tracking: Throughout fulfillment, telecom providers monitor order progress and share status updates with both customers and staff, including downstream shipping departments and scheduled technicians. This communication, often delivered via automated notifications, provides transparency about delivery timelines and potential delays to limit customer inquiries or avoid misallocated resources and labor.
- Order billing: As services go online, billing teams create customer accounts, set pricing rules, and generate invoices. Accurate billing prevents revenue leakage from untracked services and averts the potentially lasting ramifications of incorrect bills on customer satisfaction.
- Exception handling: When orders deviate from standard processes—perhaps due to custom configurations or technical issues—specialized teams investigate and resolve these exceptions. Root cause analysis helps companies identify recurring patterns and make data-driven process improvements to curtail future errors and delays.
Advantages of Telecom Order Management
The global telecom order management market size is predicted to more than double from $4.4 billion in 2024 to $11.8 billion by 2033, according to the IMARC Group. It’s no wonder: Investing in telecom order management processes and systems offers operational improvements that can increase margins and unlock other benefits:
- Manual task automation: By automating repetitive tasks across order entry, validation, routing, and returns, staff can spend more time on complex problem-solving and customer service. Automated reporting features also help speed up analyses, enhance compliance, and support process improvements.
- Increased order accuracy: Built-in validation and consistency checks increase order accuracy, preventing rework, billing disputes, technician callbacks, and returns. Automation helps companies accurately fill orders with minimal to no manual intervention, helping to accelerate service start dates and improving the customer experience.
- Faster order processing and service delivery: Parallel and automated workflows shrink activation timelines, allowing telecom businesses to deliver add-ons and digital services within hours, rather than days. Faster service delivery not only pleases customers, it also reduces time to market for new offerings, accelerates revenue recognition, and improves cash flow.
- Reduced bottlenecks and improved efficiency: Real-time order status, ongoing KPI monitoring, and intelligent routing can erase order handoff delays between departments. This helps decrease backlogs and optimizes resources within technical and customer service teams.
- Increased customer satisfaction: Transparent order tracking and reliable delivery estimates improve the quality of telecom customer experience, particularly for companies offering custom or specialized options that require more complex logistics. Satisfied customers are more likely to stay put, request additional services, and become brand advocates—all of which can lead to lower acquisition costs.
Common Challenges in Telecom Order Management
The telecom industry faces mounting pressures. The top three obstacles, according to a 2024 McKinsey analysis, are legacy business models that may not produce the profitability required to keep up with necessary investments, fiercer competition due to innovation, and a new wave of regulations driven by macroeconomic uncertainty. Prioritizing order management can help telecom companies overcome these hurdles—and others, explained below—to create more profitable operations that are ready to adapt to customer demands and market forces:
- Order fallout: When orders can’t be processed quickly due to manual errors, service gets delayed or—worse—orders fall through the cracks and remain unfilled until customers complain. This is a particular risk for nonstandard services, such as custom data center services or new internet delivery methods, that may require hours of investigation before activation.
- Complex product customization: Telecom services often involve intricate combinations of speeds, features, and bundles that can interfere with configuration and pricing. This complexity can prompt pricing errors, mismanaged inventory, provisioning mistakes, and subpar integration that may slow down fulfillment and create security vulnerabilities and inconsistent service.
- Slow processing speed: Legacy systems, manual handoffs between departments, outdated hardware, and sequential workflows cause processing delays that extend activation timelines. Severe lags damage customer satisfaction, brand reputation, and cash flow. Rushed and sloppy technical work can also increase costs due to the need for rework before service goes live.
- Meeting compliance requirements: Telecommunications providers must keep pace with evolving regulatory requirements related to consumer protection, coverage rules, and data privacy. Compliance necessitates continuous monitoring for regulatory changes, as well as regular updates in order to avoid fines and liabilities, license revocation, contract issues, and even reputational damage.
How Does Technology Enhance Telecom Order Management?
AI, automation, advanced analytics, and cloud-based ERP systems are modernizing the telecom landscape. Together, these technologies are powering a data-driven order management ecosystem that lowers operational costs, accelerates service delivery, and improves the customer experience.
ERP platforms, which centralize data and enhance order processing from initial request to service activation, create the foundation for greater automation to handle repetitive tasks, reduce human errors, and accelerate order fulfillment. Cloud-based ERP, in particular, provides telecom companies with scalability and the flexibility to handle variability in order volumes without bumping against infrastructure constraints or proportional increases in expenses. Both customers and service teams can access data from these systems for visibility into order status at every fulfillment step. Advanced analytics capabilities give decision-makers access to real-time performance metrics and predictive trends, enabling proactive order management in lieu of reactive troubleshooting.
Telecom providers are increasingly enhancing their order management with AI algorithms that analyze vast data sets to forecast demand, address bottlenecks, and identify high-risk orders. These tools predict which orders are likely to fail based on historical patterns, automatically flagging potential issues and recommending solutions before the problems have any chance of reaching customers. Generative AI has also enhanced customer service, helping companies automate responses to complex customer requests and troubleshoot issues more quickly and accurately than traditional chatbots can achieve. Businesses also leverage AI-powered automation and robotic process automation to handle such order-processing tasks as data entry, validation, and routing.
Another major advancement in order management is the adoption of Internet of Things devices and 5G networks, which together provide real-time visibility into network performance and service delivery. Integrating this level of technology into order management platforms unlocks real-time updates, remote diagnostics, and predictive maintenance data drawn directly from network equipment and customer-owned devices to extend equipment life and keep customers and support teams informed throughout the service lifecycle.
NetSuite ERP Simplifies Telecom Order Management
Telecommunications providers—especially those that rely on manual order workflows—are known to struggle with managing complex service configurations, leading to order fallout and delayed service activations. NetSuite’s unified ERP platform provides centralized multichannel order management, automated validation and routing processes, transparent inventory and compliance records, and real-time visibility throughout the lifecycle of an order. The system’s integrated billing capabilities automatically generate accurate invoices upon service activation, with flexible rules for handling complex bundles and custom configurations. Built-in analytics gives managers and sales teams intelligence into order patterns and the causes of bottlenecks to identify opportunities to decrease cycle times and operational expenses. NetSuite’s scalable cloud architecture allows telecommunications companies to handle fluctuating order volumes, accelerate innovative service offerings, and expand into new markets without overhauling their order management processes.
NetSuite’s Order Management Dashboard
As telecommunications services grow more complex, businesses in this sector must prioritize order management to meet elevated customer expectations. Providers that implement effective order management processes are more likely to deliver consistent service, even when introducing innovative bundles, entering new markets, or pursuing revenue from emerging technologies. By investing in flexible systems that can adapt to market changes, forward-thinking telecom companies transform order management from being a back-office function into becoming a competitive advantage that enhances profitability and builds customer trust through quick and reliable service.
Telecom Order Management FAQs
How does order management work for telecom companies?
Telecom order management coordinates fulfillment from initial service requests through service activation and billing. The process includes capturing requests from multiple channels, assessing technical feasibility and customer eligibility, orchestrating work across departments, and tracking progress through completion.
Is an OMS different from an ERP?
An order management system (OMS) focuses specifically on processing and fulfilling customer orders. An ERP platform often includes an OMS module that can integrate with other business operations, including finance, inventory, customer and vendor management, and HR.
Is OMS part of CRM?
CRM systems are designed to manage customer relationships—collecting information about interactions, preferences, purchase history, and sales opportunities—while an order management system (OMS) handles the transactional aspects of customer order fulfillment. Comprehensive ERP platforms integrate these complementary capabilities, with CRM modules managing customer relationships and sales while the OMS executes order fulfillment.








