Many businesses have volumes of internal and external data at their disposal, yet their leaders continue to make decisions based on gut, past experience or one-dimensional analysis. In the past, analyzing data that resides in disparate, disconnected systems has been difficult and time-consuming. Advanced analytics — the next level of business intelligence — changes that by uncovering patterns and prescribing actions to achieve a desired result. Such sophisticated, automated analysis is no longer the domain of only large businesses, either. Here’s what advanced analytics can do for growing businesses, too.
What Is Advanced Analytics?
Advanced analytics describes the analysis of data using complex techniques to forecast trends and predict events. It uses state-of-the-art tools, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, along with various statistical analyses and algorithms, to examine large data sets. The goal is to identify patterns and discover deeper insights that go beyond traditional BI. Descriptive, diagnostic, predictive and prescriptive analytics, as well as data mining and other advanced, high-level data science methods, all fall under the advanced analytics umbrella.
Advanced Analytics vs. Business Intelligence:
Advanced analytics and BI are both tools that help a company make sense of its raw data to understand its current standing, where it’s heading and to inform decision-making. But the terms are not interchangeable because each one prioritizes data differently.
What is business intelligence?
Business intelligence refers to the technologies and strategies involved in collecting and analyzing data from internal and external systems to provide a detailed view of a business’s current standing. Using reports, dashboards and query tools, companies can mine historical data and run templated and custom reports. BI is a powerful tool that provides real-time access to a company’s underlying data to drive informed, real-time decision-making.
Key differences:
Advanced analytics and business intelligence are related but not one and the same. Three key characteristics highlight their differences:
-
Direction: BI tends to focus on historical data to identify what has happened and why. It’s a reactive, rearview mirror approach. Advanced analytics takes a proactive, forward-looking approach that extrapolates data to forecast what could happen and how various actions might alter an outcome. It asks what will happen? In marketing, for example, BI can measure a campaign’s effectiveness — how many people clicked on an online ad, signed up for an email, bought a product, etc. Advanced analytics provides insight about customer preferences, opportunities for upselling and who to market to going forward.
-
Methods: BI uses basic calculations and predefined formulas, but its end product requires human interpretation to support decision-making. Advanced analytics draws upon the world of data science, combining elevated methods such as statistics, quantitative analysis, predictive analytics and text analytics to help drive automated decision-making.
-
Data: BI uses structured data from a single source, facilitating summary reporting and drill-down capability. BI tools typically sit on top of a data warehouse or data mart. Advanced analytics taps structured and unstructured data from disparate systems. Examples of unstructured data include video, text, social media comments, reviews and images. Advanced analytics cleanses and prepares the data for analysis, beyond simply collecting it.
Key Takeaways
- Advanced analytics makes sense of data and provides forward-looking, actionable insights.
- Advanced analytics is a more complex, forward-looking and expansive facet of business intelligence.
- Advanced analytics uncovers ways businesses can improve their operations.
- The future of advanced analytics is bright, bolstered by developments in technology, including cloud computing.
Advanced Analytics Explained
Advanced analytics uses sophisticated, automated methods to assess data, revealing correlations and relationships and extracting predictive information. Data mining, which sorts large quantities of diverse data into clean, usable data, is key to this process. Additional techniques include semantic analysis, sentiment analysis, network and cluster analysis, multivariate statistics, graph analysis, simulation, complex event processing and neural networks. Advanced analytics is supported by machine learning, artificial intelligence and pattern-matching that pulls out information from numerical and text data.
Advanced analytics uses dashboards and reporting tools to help businesses understand their data in an intuitive way. Reports can be run as needed on an ad-hoc basis or on a regular schedule. Advanced analytics also uses data visualization tools, such as graphic elements like charts and maps, so the analysis is easier to understand. These tools all support data-driven decisions.
Why Is Advanced Analytics Important?
Advanced analytics provides businesses with deeper insight into patterns and behavior that can result in predicting future action. It offers a significant strategic advantage by uncovering, for example, new business opportunities and innovations, a detailed understanding of customer and employee behavior, new ways of looking at old problems and areas for operational improvement — all of which can improve revenue or reduce cost.
For example, with supply chain analytics, you can analyze data in real time and receive alerts to signal potential inventory issues before they turn into bigger problems. Advancements in data storage and cloud computing have helped make advanced analytics accessible and affordable to businesses of all sizes.
What Is the Value of Advanced Analytics?
Advanced analytics has the potential to create value across an entire organization, from customer-facing areas to the back office. It unlocks the treasures hidden within the volumes of data acquired through multiple platforms, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM) and human resources (HR) systems. Because the information created by advanced analytics is forward-looking, it can help a company capture revenue opportunities, save money and reduce risk. Some examples:
- Advanced analytics can help marketers better target and increase the effectiveness of their campaigns based on a more intimate knowledge of customer tendencies.
- Advanced analytics can predict equipment failure from wear and tear, informing repair and maintenance schedules and reducing downtime.
- Advanced analytics can provide human resource managers with early warning signs of employee dissatisfaction, reducing staff turnover and its many associated costs.
Types of Advanced Analytics
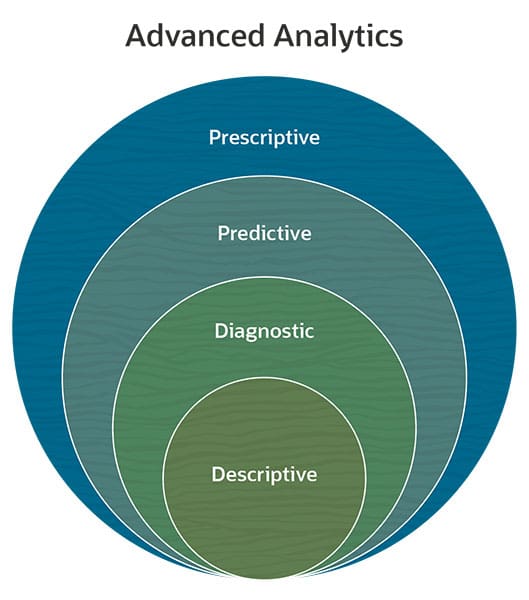
Advanced analytics falls into four categories based on the business question it helps to answer, such as “what happened?” and “what’s likely to happen?” Each type comprises a variety of analysis methods to achieve its purpose.
-
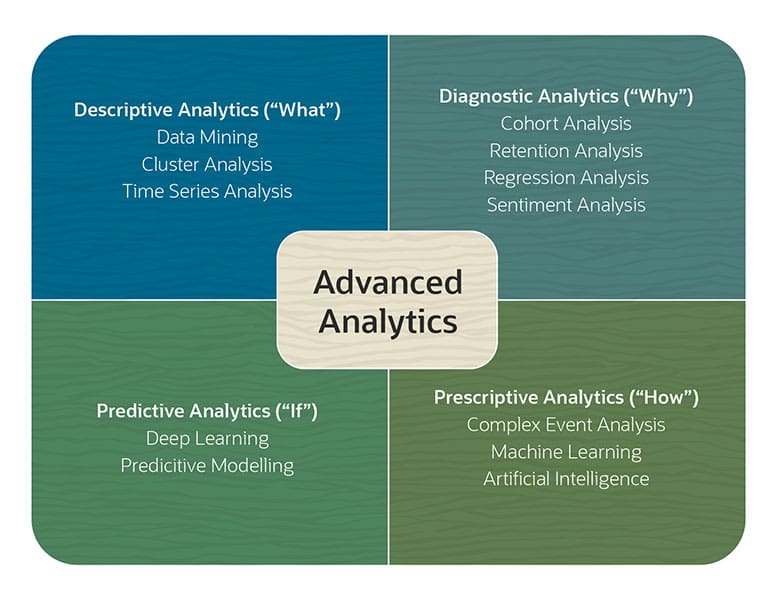
Descriptive analytics: The simplest of the four types, though still quite complex, descriptive analytics focuses on the aggregation of data to form a profile that describes what happened. Data and text mining, cluster analysis and summary statistics are methods used.
-
Diagnostic analytics: Diagnostic analytics answers why something happened. Like descriptive analysis, it centers on past events. It attempts to link cause and effect using such methods as regression analysis, sensitivity analysis and principal component analysis.
-
Predictive analytics: Looking forward, predictive analytics attempts to estimate what could happen if certain conditions are met. Rooted in probability, predictive analytics uses quantitative analysis, predictive modeling and deep-learning techniques.
-
Prescriptive analytics: Generally considered to have the most potential business value, prescriptive analytics focuses on how to achieve a particular outcome. It’s the most actionable of the four types of advanced analytics because it points the way to desired outcomes. It also relies on the most complex analysis methods, such as simulation analysis, artificial intelligence, machine learning and neural networks.
Benefits of Advanced Analytics
Deeper insights and data-driven recommendations provided by advanced analytics create “softer” benefits within the decision-making process that go beyond the actual value derived from the decisions themselves. They impact company culture, which can bolster a business’s financials over the long term.
-
Less time on reporting, more time for strategy
Advanced analytics frees employees to concentrate on other valuable work. By automating data sorting, cleaning and analysis more time can be spent on strategic endeavors.
-
More accurate decision-making
Fact-based information typically results in better decision-making than decisions based on intuition or experience alone.
-
Encourages progressive thinking
Advanced analytics helps business leaders take a more proactive and anticipatory approach to managing operations. Their lines of sight are extended, which trickles through the entire organization.
-
Better ROI
Advanced analytics can help grow top-line revenue resulting from a more intimate knowledge of customer preferences and habits. It also can improve business efficiency by anticipating and reducing operational risks, which leads to cost savings.
-
Increases personalization
Using deep, customer-specific data generated by advanced analytics, sales and marketing can shift their efforts from generalized customer segment interactions to personalized engagement.
-
Empowers users to share data
Advanced analytics brings together siloed information so business leaders and employees can share and align on the data. For example, you can go in depth on your supply chain and how delays may impact future prices and inventory levels. Workers also can spend more time collaborating on solutions, rather than arguing over whose numbers are “right.”
-
Emboldens innovation
Predictive analysis provides a statistical confidence level, which means business managers can worry less about misreading a situation and focus more on introducing innovative new strategies, products and services.
What Are Advanced Analytics Techniques or Capabilities?
Advanced analytics relies on a host of mathematical and statistical techniques for interpreting data within its four categories of analytics: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive and prescriptive. Exaples of specific techniques include data mining, regression analysis, sentiment analysis, cluster analysis and machine learning — more on those soon.
Such techniques typically required highly trained professionals with backgrounds in all aspects of data science or coding experience in languages like Python and R. However, modern advanced analytics soltions are fitted with intuitive dashboards, drag and drop reporting and graphic interfaces, making them easy to understand by business users.
Use Cases for Advanced Analytics
Across multiple industries, many different business functional areas can benefit from advanced analytics. From marketers to doctors and from retail to manufacturing, a trend in ERP platforms is using advanced analytics to gain a competitive advantage through deeper understanding of customer behavior and operational efficiencies. Some real-world examples include the following.
-
Retail: More efficient inventory management and development of dynamic online product recommendations by identifying products that customers tend to buy together.
-
Health care: Identifying patients with certain risk factors and suggesting treatment or early detection for potential health issues.
-
Media: Targeted advertising campaigns based on the likelihood of user interaction.
-
Entertainment: Optimizing video-stream schedules based on customer preferences and viewing patterns.
-
Consumer goods: Gaining actionable insights from online product reviews, such as identifying customers likely to churn.
-
Wireless telecom: Predicting potential network failures to better schedule preventive maintenance.
-
Manufacturing: Workforce management tactics, such as predicting labor needs based on forecasted demand to optimize workforce schedules.
10 Advanced Analytics Techniques
So how does advanced analytics do what it does? It employs heavy-duty quantitative and qualitative techniques to uncover relationships, trends, correlations and outliers. Each of the following techniques approaches data in its own way:
-
Data mining: Looks for hidden patterns, relationships and anomalies within large sets of data to predict future trends.
-
Machine learning: Autonomously uses algorithms to find patterns in data and develop predictive models to analyze future outcomes.
-
Cohort analysis: Groups data based on shared user behaviors over a particular time span to understand their actions and compare one group to another.
-
Cluster analysis: Groups data based on similarities. It’s a typical first step before applying other techniques.
-
Retention analysis: Incorporates other techniques, like cohort analysis, to explore how well a company holds onto its customers and gains new ones over time.
-
Complex event analysis: Analyzes data from current events, changes in business conditions and surrounding circumstances in real time to uncover opportunities and threats.
-
Predictive analysis: Draws on many other techniques, including data mining and machine learning, to analyze historical data to forecast future outcomes, usually through the creation of predictive models.
-
Regression analysis: Identifies dependent and independent variables in a data set, how they impact each other and what their future relationship is likely to be.
-
Sentiment analysis: Sorts and understands text to interpret embedded emotions and determine an overall attitude (positive, negative or neutral).
-
Time series analysis: Sequences data to measure the same variable over time, identifying trends, seasonality and cyclic patterns.
Technology and Tools for Advanced Analytics
The promise and value advanced analytics brings to a business can be transformative. However, it’s not without its complexities, which is why choosing the right advanced analytics technology is critical. A company needs to identify the data it wants to analyze and how it’s captured and housed, along with the security and governance that surround it. It’s important to consider business users’ backgrounds and savvy in order to select tools that are both intuitive and robust. The information obtained from advanced analytics is often best absorbed through visualizations presented in a context that makes sense for the business. Whether housed on-premises or in the cloud, the best advanced analytics technology and tools democratize their insights for greater business use.
Future of Advanced Analytics
Advanced analytics are here and the market is growing; one Market Study forecast pegs its value at $165.68 billion by 2025, representing a 33% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) since 2017. The technologies behind it, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, continue to evolve, becoming more predictive over time. And with no shortage of data in sight — global market intelligence firm IDC predicts the amount of data created and replicated will grow at a CAGR of 23% from 2020 to 2025 — the opportunities for more detailed analyses based on even bigger data sets continue to swell. In parallel, all of this data can be cost-effectively stored and analyzed in the cloud on a subscription basis, bringing advanced analytics that would otherwise be out of reach to growing businesses into the heads of many.
Conclusion
Many organizations are sitting on an ever-growing mountain of data whose ultimate power — predicting the business’s best future direction — lies out of reach. Enter advanced analytics, which, using sophisticated tools, statistical analyses and algorithms, can not only make sense of the data that resides across multiple company platforms, but can also provide deep insights into business patterns and customer behaviors to help forecast trends and predict future events.
This knowledge provides any business with a competitive advantage if it was an advanced analytics platform, helping it realize new opportunities, avoid potential problems and embrace innovation — among many more benefits that can improve revenue and lower expenses.
Advanced Analytics FAQ
Q: What is advanced data analytics?
A: Advanced analytics describes the sophisticated analysis of data using complex techniques to forecast trends and predict events. It uses state-of-the-art tools, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, and complex statistical analyses and algorithms to examine big data and identify patterns to discover deeper insights that go beyond traditional business intelligence (BI).
Q: What is the difference between analytics and advanced analytics?
A: Analytics, such as business intelligence, examines historical, structured data to understand what has already happened. Advanced analytics looks forward, using a data-science-driven approach that leverages structured and unstructured data to predict future outcomes and prescribe action.
Q: What are advanced analytics tools?
A: Advanced analytics uses quantitative and qualitative methods to uncover relationships, trends, correlations and outliers. Tools to do so include data mining, machine learning, cohort analysis, cluster analysis, retention analysis, complex event analysis, predictive analysis, regression analysis, sentiment analysis and time series analysis.









