Every company needs to be sure that its business strategy and operational processes are in tight alignment, that it’s investing resources sensibly and that it’s meeting or exceeding its financial goals. Such confidence comes from the sound planning, budgeting and monitoring of key performance indicators that illuminate the company’s progress toward its objectives. This is the realm of enterprise performance management (EPM). Read on to gain a comprehensive understanding of the process, its benefits, related trends and how to select the right EPM solution.
What Is Enterprise Performance Management (EPM)?
Enterprise performance management (EPM) is a set of business processes and software that helps organizations align their strategies across all departments to manage and improve their overall performance and to achieve strategic goals.
Without proper execution, even the best business strategy can fall flat. EPM supports a business’s efforts to reach its goals by monitoring, measuring and analyzing financial performance based on clearly defined, quantifiable metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs). EPM also encompasses the technologies that enable these efforts, such as data collection and analysis.
EPM is typically described in terms of financial management — and rightly so. Financial teams rely on EPM for planning, budgeting, forecasting, scenario modeling and reporting. EPM also helps them more quickly reconcile accounts and close the books at the end of a financial period. But EPM can also be used by other functional areas of the business, such as manufacturing, marketing and human resources (HR), to align their strategies and operations, allocate resources, manage risk and analyze their performance.
EPM vs. ERP
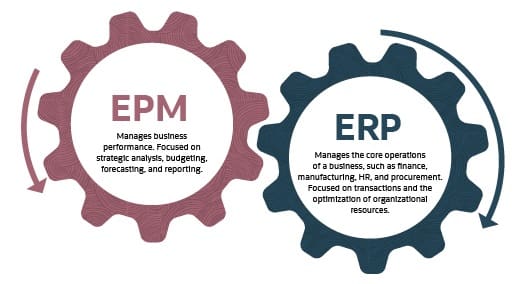
EPM and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems serve related, yet distinct, purposes. EPM manages business performance, focusing on strategic analysis, budgeting, forecasting and reporting. Its performance insights are built on top of data from an ERP system, which automates and optimizes the business’s day-to-day operating activities, such as finance, accounting, sales and inventory management. Together EPM and ERP support practices that align finance with operations for integrated business planning.
Key Takeaways
- EPM as a process monitors financial performance and aligns a business’s overall strategy with planning and execution.
- EPM as a technology speeds financial processes, including budgeting, account reconciliation and closing the books.
- Advanced analytics and real-time performance monitoring are among several EPM trends driving adoption.
Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) Explained
EPM is both a process and a technology that helps business leaders determine how well the company is performing against its forecasts and goals. An EPM solution captures, consolidates and analyzes performance data across various functions and departments so that leaders can respond quickly to changing circumstances. These tools, typically managed by the finance department or chief financial officer (CFO), help management evaluate and allocate resources, optimize performance and reap the most from the company’s investments.
More specifically, EPM helps a business:
- Connect and consolidate data across the entire organization and eliminate manual tasks, so that finance teams don’t have to run the numbers separately for each department.
- Model different scenarios, such as a merger or possible economic shift, to analyze and prepare for possible business outcomes.
- Identify data trends and correlations to improve forecasts.
- Increase visibility throughout the organization, using reporting and real-time dashboards to minimize surprises.
- Manage data governance automatically.
Ultimately, EPM helps managers plan (using historical data and forecasting), monitor and report (relying on KPIs) and analyze financial performance. It’s an iterative process sometimes referred to as business performance management, corporation performance management, integrated business planning or financial performance management. (The standalone phrase “performance management” is not related to EPM. Rather, it’s a human resources matter that includes talent acquisition, benefits administration and workforce planning.)
Why Is Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) Important to Businesses?
EPM offers businesses a strategic framework that affirms their overarching objectives are in sync with their day-to-day operations. It helps them set departmental goals and then accurately measure, analyze and report performance toward those goals based on real-time operational and financial data. EPM insights are considered mission-critical because they help businesses improve operational processes, boost productivity, refine budgets and forecasts, manage risk, remain competitive and, thereby, thrive.
EPM Business Processes
EPM encompasses five main processes that help businesses understand how well they are meeting their operational and financial performance goals. They include the following activities, all of which can be made more efficient through the use of automated EPM software.
- Strategic modeling is the process of developing the business’s long-term goals by weighing different scenarios and outcomes and their impacts on operational and financial performance. Revenue, sales and cash flow are among the key considerations, as is the careful selection of KPIs that best track performance over time, such as gross profit margin and the variances between budget and actual results.
- Planning and budgeting is the process of creating financial and operational plans to accomplish the business’s strategic goals. It involves setting financial targets, forecasting revenue and expenses, and allocating funds to various initiatives. Underlying this process is the need to manage costs, maintain positive cash flow and ensure a healthy profit margin.
- Consolidating and closing occur at the end of an accounting period, such as a month or quarter. Data from across the business is collected, reconciled and consolidated into the company’s financial statements, which include the income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statement. Once the statements are finalized, the business can close its books for the period.
- Reporting is fundamental to communicating the business’s financial performance to key stakeholders, including management and external parties such as tax authorities, regulatory agencies, investors and lenders. These stakeholders rely on the information found in financial statements, annual reports and other documents to guide their decisions, such as whether to invest in the business.
- Analyzing performance is a continuous process in which businesses evaluate their operational and financial achievements relative to their strategic goals. KPIs are scrutinized, actuals are compared to targets, variances are investigated and trends across accounting periods are assessed. These analyses provide insights that can be used to fuel future plans, forecasts and projections.
5 EPM Business Processes
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Strategic modeling | Developing business goals in light of possible scenarios and their impact on performance. |
| Planning and budgeting | Creating financial and operational plans to achieve strategic goals. |
| Consolidating and closing | Collecting, reconciling and consolidating financial data, then closing the books for an accounting period. |
| Reporting | Communicating business performance to internal and external stakeholders via financial statement, annual reports, etc. |
| Analyzing performance | Evaluating how well the business met its strategic goals to inform future performance plans. |
Benefits of an Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) System
EPM systems provide many benefits that can help businesses improve their performance, respond to change and increase profitability. Here are some vital EPM advantages:
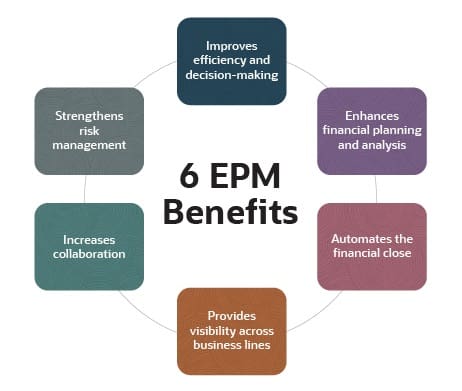
- Improves efficiency and decision-making: The vast amount of data that must be collected, consolidated, crunched and closed on from across the business makes manual processes impractical from the perspectives of both accuracy and timeliness. EPM systems automate the business processes described in the previous section, boosting real-time decision-making.
- Enhances financial planning and analysis: EPM systems improve financial planning and analysis so that the business can realistically set, plan for and reach its performance goals.
- Automates the financial close: EPM systems automate the many accounting steps that culminate in closing the books at the end of a financial period. Automation minimizes the amount of manual work, improves accuracy and shortens the time to close, allowing business managers to concentrate on analyzing company performance.
- Provides visibility across business lines: EPM systems connect business divisions, providing leaders with a holistic, transparent view of enterprise performance. This helps them align plans and develop forecasts that can respond to changes in the market while continuing to grow the business.
- Increases collaboration: EPM systems facilitate communication and collaboration across a business’s departments and teams, ensuring that everyone is working toward common goals and objectives.
- Elevates risk management: EPM systems help businesses recognize potential issues and respond quickly to minimize negative financial and operational impacts.
EPM Examples
The worldwide market for EPM applications reached $6.3 billion in 2022, according to IDC. The researcher attributed EPM’s growth — 8.7% in 2022 — to an increased need for the “differentiating value of decision making and planning agility,” which, in turn, is fueling the need for features like cross-functional planning, contingency planning, scenario planning and constraint-based analysis.
Indeed, businesses from all industries are employing EPM systems to help manage performance. Here are two examples.
- Life sciences company Thermo Fisher Scientific was managing rapid growth. But diverse teams in different regions were working on siloed systems with their own KPIs, which hampered collaboration, impeded strategic planning and reporting, and made it difficult to view and act on data in near real time. EPM enabled Thermo Fisher to centralize data from across the business on one platform, greatly improving its planning, budgeting and forecasting capabilities, as well as its ability to respond and adjust to changing business needs.
- At BISSELL, a manufacturer of home cleaning products, a reliance on spreadsheets created numerous business inefficiencies, data management headaches and difficulty in long-term planning. Employees were frustrated, too. The company decided on an EPM system to streamline its financial planning and reporting processes and gain better visibility across the business. Automation of previous manual tasks sped data consolidation, planning and reporting, the latter to the tune of one-third of the time required for generating reports prior to EPM deployment.
History of EPM
The desire to optimize business operations and make good financial decisions has been around for as long as businesses have existed. Computerized spreadsheets, beginning with VisiCalc and Lotus 1-2-3 in the late 1970s and early 1980s, gave businesses a technology-based method for financial and operational planning. In addition to database integration, these tools permitted planning, budgeting and forecasting capabilities. While slow and crude by today’s terms, early spreadsheets gave organizations the ability to monitor KPIs, perform analysis and automate reporting across disparate departments. Email and other connected technologies made human collaboration easier, including working together on financial reports, account consolidation and automated database updates.
The first products identifiable as EPM software originated in the 1990s, starting as extensions of enterprise accounting applications. Gradually, these systems evolved from client/server systems to internet-enabled, web-browser-based applications. Today many EPM applications run in the cloud, for ease-of-use (think: employees working remotely), support boons (think: the vendor maintains the application) and lower upfront costs.
5 Key Enterprise Performance Management Trends
EPM adoption is on the rise, up from 54% of organizations in 2022 to 62% in 2023, one study shows. Small and midsize businesses account for a large portion of this growth. Among the EPM trends helping to fuel this growth are:
- Advanced analytics: By applying advanced analytics and data-science techniques, such as machine learning, to financial and operational data, EPM can provide deeper insights and predictive capabilities that improve financial plans and forecasts.
- Real-time performance monitoring: Real-time data and performance monitoring in EPM allow organizations to actively monitor a multitude of business processes and make faster decisions based on newly emerging trends and insights.
- Integrated financial and operational planning: EPM systems mesh financial and operational planning to provide a holistic view of an organization’s performance and resources. By linking financial and operational metrics, EPM fosters a collaborative approach to planning and performance management.
- Cloud adoption: Many organizations have embraced the cloud for their business systems. Cloud-based EPM solutions have significantly lower upfront costs, can scale as demand dictates and are easily accessible from multiple locations.
- Enhanced user experience: EPM solutions with user-friendly interfaces encourage companywide adoption. With interactive dashboards and visualization capabilities, EPM software provides easy-to-digest performance data that facilitates better decision-making.
Choosing the Right EPM Solution
For EPM to work most efficiently as a process, businesses need an EPM system that gathers and interprets large amounts of data and disseminates it to stakeholders for informed decision-making. The EPM selection process begins with a comprehensive needs assessment, which helps to clarify the types of features needed in the solution. Generally speaking, an EPM solution should be able to support:
- Financial basics for historical and future data: Look for an EPM tool that streamlines and supports essential financial management tasks, such as creating and tracking annual budgets, account reconciliation, closing the books and creating financial statements.
- Operational data: EPM tools should be able to create, manage and report on project budgets, marketing expenses and workforce estimates, for example, with context from earlier analyses so that future decisions take real-world lessons into account.
- Tax reporting and other compliance issues: An EPM system should keep all the company’s data in sync. Doing so ensures tax calculations are up to date, leading to the faster creation of accurate financial reports and compliance with government requirements.
- Sales tracking: Among the essential data EPM can gather and analyze are sales, revenue and expense forecasts, by department or business segment. This lets the business identify which segments are most profitable, diving into categories by customer type or product.
- Reports: Reports should be understandable for every stakeholder, including nonfinancial specialists. Beyond numbers, they should offer context for forecasts in sales, expenses, market demand and project management.
Additional considerations when choosing an EPM solution include whether the system can integrate with other business software, how the system can be deployed (cloud vs. on-premises vs. hybrid), whether the vendor has the right expertise and offers training and support, and whether the system can be customized. Last but not least is how much an EPM system costs, what pricing includes and how long it will take to realize a return on the investment.
Get the Benefits of EPM With NetSuite
NetSuite Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) is a newcomer to the NetSuite family of software solutions, connecting and automating a business’s many financial processes for more efficient operations. The comprehensive solution packages new and existing NetSuite tools — namely, Planning and Budgeting, Account Reconciliation, Narrative Reporting, Profitability and Cost Management, and Corporate Tax Reporting — that together automate workflows, increase business visibility, inform strategic decision-making and drive business growth. NetSuite EPM was built from Oracle Fusion Cloud EPM and seamlessly integrates with NetSuite Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP).
EPM connects a business’s strategic goals and daily operations to help ensure that both parts are in sync. It measures progress so that course corrections can be made along the way toward corporate goals, identifies emerging trends in the business and automates financial processes, including budgeting, account reconciliation and closing the books. EPM helps finance teams, CFOs and other managers perform their jobs more efficiently and make better decisions with greater confidence.
EPM FAQs
What is the difference between ERP and EPM?
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) and enterprise performance management (EPM) oversee related but different aspects of a business. ERP systems automate core operational processes and oversee day-to-day transactional activity. EPM software focuses on the performance of those processes and involves planning, budgeting, forecasting and reporting to ensure outcomes align with the company’s strategic goals.
What is the purpose of enterprise performance management?
Enterprise performance management (EPM) enables organizations to connect their strategies and operations to better analyze business performance. EPM covers specific processes involving planning, budgeting, forecasting and reporting.
What is an enterprise performance framework?
An enterprise performance framework helps companies monitor their business performance to optimize what they are doing right and improve areas where they may be lagging.
What are the key components of enterprise performance management?
Key components of enterprise performance management (EPM) include development of a business strategy, planning and budgeting, monitoring and analysis of key performance indicators, and reporting to stakeholders.
What is a performance management framework?
A performance management framework is a structured approach to planning, monitoring, analyzing and improving business performance. It can be applied to all areas of the business, such as finance, inventory and human resources.








