Enterprise performance management (EPM) can unleash the power of data to spur businesses to new heights. By integrating and automating the collection and analysis of financial and operational data, companies that adopt EPM stand prepared to tame risk and seize opportunity in today’s volatile marketplace.
Each new wave of technology — from big data to cloud computing and now artificial intelligence (AI) — has increased the benefits of EPM as companies have more and more data to collect and analyze. Technological innovation has also brought this best practice within reach for more small to midsize businesses, so they can make real-time, highly informed decisions that support their strategic goals.
What Are the Benefits of EPM?
Companies that trade in their old-school spreadsheets and fragmented data systems for enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions are laying the groundwork for EPM. From there, EPM brings together planning, budgeting, forecasting, account reconciliation, financial close and reporting processes from across the entire organization to help businesses improve the speed and accuracy of financial processes and gain the insights they need to enhance decision-making. What’s more, all processes operate from a single, unified source of real-time data. The benefits that then flow, day in and day out, include budget accuracy, streamlined financial closings, regulatory compliance and overall cost management.
EPM can also automate data collection and analysis to run “what if?” scenarios regarding products, operations and strategic planning. It can gather the latest internal and external information to address questions that could determine profit or loss: How could inflation increase the cost of raw materials? What if the competition poaches a key customer? What might force a pivot to a new business model?
Key Takeaways
- EPM integrates, automates and streamlines financial and operational data from across departments.
- Analytical tools, including AI, parse up-to-date business information to drive better decision-making.
- Routine processes, such as a company’s financial close, run more collaboratively and smoothly with EPM.
EPM Benefits Explained
Today’s businesses run on key performance indicators (KPIs). ERP systems act like perpetual KPI machines, as retailers measure foot traffic in their stores, manufacturers track defect rates and service providers monitor customer churn data. Running on top of ERP systems, EPM plugs these and myriad other KPIs into financial planning and analysis processes across the company in real time to understand and report on a business’s performance against strategic goals, such as efficiency and growth.
Look at it this way: ERP systems are designed for operating a business and its day-to-day transactions, while EPM is designed for managing the business with strategic analysis and reporting. The benefits of EPM become increasingly important in times of volatility when market conditions can rapidly erode a company’s performance. In Deloitte’s 2023 Mid-Market Technology Trends Report, midsize companies responding to a survey ranked optimizing business operations and enabling business growth in their top tier of technology objectives. Deliverables like these are what EPM was made for.
EPM builds on other practices, such as business intelligence and adding analytical capabilities in the era of AI. In industry jargon, EPM may also go by names like corporate performance management and integrated business planning.
Financial Benefits of EPM
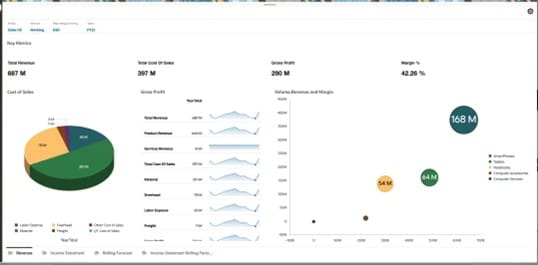
EPM incorporates operational data into financial planning, forecasting, budgeting, account reconciliation, financial close and reporting. As a result, finance departments are most likely to become EPM power users, although more line-of-business and department heads have begun to use it, too. Financial benefits of EPM include enhanced budget accuracy, real-time forecasting adjustments, a streamlined financial closing process, compliance with regulatory requirements, the ability to identify profitable products/services and cost management.
-
Enhanced Budget Accuracy
A budget’s usefulness to a company depends on accurate data, current information, forward-looking analysis and built-in flexibility. EPM automates data collection from across the company on a unified cloud platform, avoiding errors inherent in manual data entry and reentry from one system to another. Information becomes transparent to all. And because the data is continually refreshed, budgets can reflect the state of the business in real time. Then, using more dynamic budgeting approaches, such as driver-based planning, scenario planning and rolling forecasts (all described below), companies can allocate resources based on business performance and changing market conditions. This approach represents a marked change from traditional procedures that create static annual budgets that companies check throughout the year for adherence to myriad line items.
-
Real-Time Forecasting Adjustments
Companies can no longer run their businesses based on annual budgets whose assumptions begin aging the moment they’re printed. Nor can they plan ahead based only on historical performance data. To improve decision-making, EPM enables dynamic forecasting based on real-time business input and predictive analytics. This can involve one or more of three techniques:
- Driver-based planning: This cause-and-effect exercise analyzes financial statements to pose the question: “What’s driving this line item?” The answers, ranging from internal business inefficiencies to external competition, lay the groundwork for forecasting and scenario planning.
- Rolling forecasts: This forecasting approach enables continuous updating of planning and budgeting assumptions. Using add/drop sequencing, a company might set a rolling forecast period of 12 months. This means, for instance, that after recording performance for November 2023, the forecast year would move forward to begin in December and end the following November. As the forecast horizon continually rolls forward, companies can more reliably project future outcomes based on current performance instead of old data. Applying AI and predictive analytics further sharpens forecasts.
- Scenario planning: “What if?” scenarios are fueled by driver-based planning and rolling forecasts, as described in more detail below.
-
Streamlined Financial Closing Process
Companies often struggle to produce their single version of truth — aka financial statement — on strict deadlines. The pressure is on every month, quarter and/or year, depending on their board, management, stakeholders, banks, regulators and other demanding audiences. But when company data is dispersed in various formats across fragmented systems and spreadsheets, pulling it all together makes the financial close an arduous task that is prone to error.
EPM draws operational as well as financial data into a unified platform, automates manual tasks and improves the flow of information across the company. For instance, account reconciliation between accounting records and external statements, such as invoices, can take place on an ongoing basis, avoiding a last-minute scramble to close the books. In another example, EPM enables financial software to automatically flag potential errors so that finance team members working on the close can narrow their focus to exceptions instead of analyzing innumerable transactions.
-
Compliance With Regulatory Requirements
EPM can help a company stay compliant with regulatory requirements. And it can help analyze the impact of changing regulations on the business. In the first case, EPM software includes standard templates, KPIs and workflows for many common reports — for example, for the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), other financial regulators and tax authorities. EPM software can also be customized to meet industry-specific reporting standards. Meanwhile, transaction monitoring, audit trails and automatic flagging of discrepancies help minimize fraud, noncompliance and other risks. And when it comes to forecasting regulatory risk, scenario planning exercises can simulate rule changes so that companies can plan for the potential impact on their business.
In all cases, EPM’s elimination of data silos enables visibility, accuracy, consistency and, therefore, adherence to rules and regulations. Narrative reporting features in the software also let companies link financials with contextual reporting and explanations, all in one report.
-
Identifying Profitable Products/Services
As EPM provides better visibility and insight into all aspects of the business, both finance departments and business-line managers can drill down into the performance of individual products and services at all stages of their life cycle. Here are three ways EPM helps companies separate profitable offerings from the nonstarters in their existing product portfolios and prepare for their next product launch:
- EPM can run scenarios for new products and services that integrate market research, cost considerations and other factors to determine their potential to succeed in the market.
- Then, EPM can continuously monitor direct and indirect costs, sales data and other KPIs to inform product repositioning.
- From there, financial modeling can help forecast the impact of different business tactics on product profitability, such as new sales incentives, different channels to market or changing prices.
-
Cost Management
By centralizing data across financial and operational departments on one platform, EPM automatically tracks costs more closely than periodic, manual efforts to align different business units’ multiple spreadsheets and nonstandard data systems. Preset thresholds, dashboards and alerts can draw immediate attention if costs start veering out of control. Predictive algorithms can analyze performance against budgets and plans, including root causes of budget overruns, to identify potential savings. These efforts fuel rapid decision-making on whatever reallocations or cuts may be needed to improve the alignment of costs with business objectives.
Operational Benefits of EPM
There are two ways to look at the operational benefits of EPM. One addresses the finance department’s efficiency, while the other applies to other parts of the company. Either way, EPM provides a range of benefits, including workflow automation, a reduction in operational bottlenecks, real-time performance tracking and benchmarking against industry standards.
-
Workflow Automation
Efficient workflows minimize the waste of staff time and other resources, increasing productivity and profit margins. EPM in the finance department automates routine tasks to reduce manual labor and decrease errors in data entry, aggregation and processing during complex procedures, such as the financial close. In turn, finance professionals can shift their focus to more value-added work, including collaborating with business-line leaders to improve performance. Likewise, managers in sales, human resources, product and other departments increasingly use EPM to enhance their own workflows. For instance, supply chain managers can consolidate data from their company’s manufacturing floor across suppliers, logistics providers and customers to track KPIs and analyze trade-offs, such as speed of delivery vs. cost.
-
Reduction in Operational Bottlenecks
Bottlenecks in any part of a company can limit profit potential, increase costs and decrease customer satisfaction. In the finance department, a company’s accounting procedures can be rife with these pain points — especially if the team lacks visibility into companywide information, including inventory levels, project milestones and the status of fixed assets. EPM’s integration of operational and financial data eliminates bottlenecks like these, facilitating financial planning, analysis and reporting. Continuous accounting spreads out the work over time. By embedding accounting into business units’ contract management, for instance, revenue recognition can become part of a company’s daily routine, rather than creating a logjam at the end of every accounting cycle.
Other departments can also use EPM for their own performance analysis. In supply chain management, the combination of real-time monitoring with analytics can identify distribution bottlenecks and their financial impact related to transportation shortages, production delays and demand spikes, for example.
-
Real-Time Performance Tracking
Business and finance executives can make more informed, timely decisions with access to real-time performance tracking. EPM dashboards and KPIs visualize problems and opportunities. Summary snapshots allow drilldowns to transaction-level details. Embedded analytics deliver insights, and AI lends predictive capabilities to guide decision-makers to better outcomes. For example, if product sales in one region are exceeding expectations and risking stock outages, action can be taken to shift inventory from stores with lower sales. Then, an analysis could unearth best practices from the high-performing region to be replicated across the country.
-
Benchmarking Against Industry Standards
Benchmarking against the competition represents a time-tested tactic for gauging and improving a company’s own performance. Regardless of industry, top KPIs for comparison measure profitability, leverage, valuation, liquidity and efficiency. Beyond that, industry-specific KPIs vary. For example, manufacturers measure and compare how quickly and efficiently they convert investments in fixed assets and inventory into cash, using KPIs known as fixed-asset turnover and inventory turnover.
Sources of external data may range from competitors’ filings with the SEC, to market research reports, to the hired services of boutique benchmarking firms. In turn, EPM tools gather and analyze internal KPIs against this business intelligence. In a financial context, benchmarking might help a company identify potential improvements in the size, cost and efficiency of its finance function, framework for internal controls and management of working capital.
Strategic Benefits of EPM
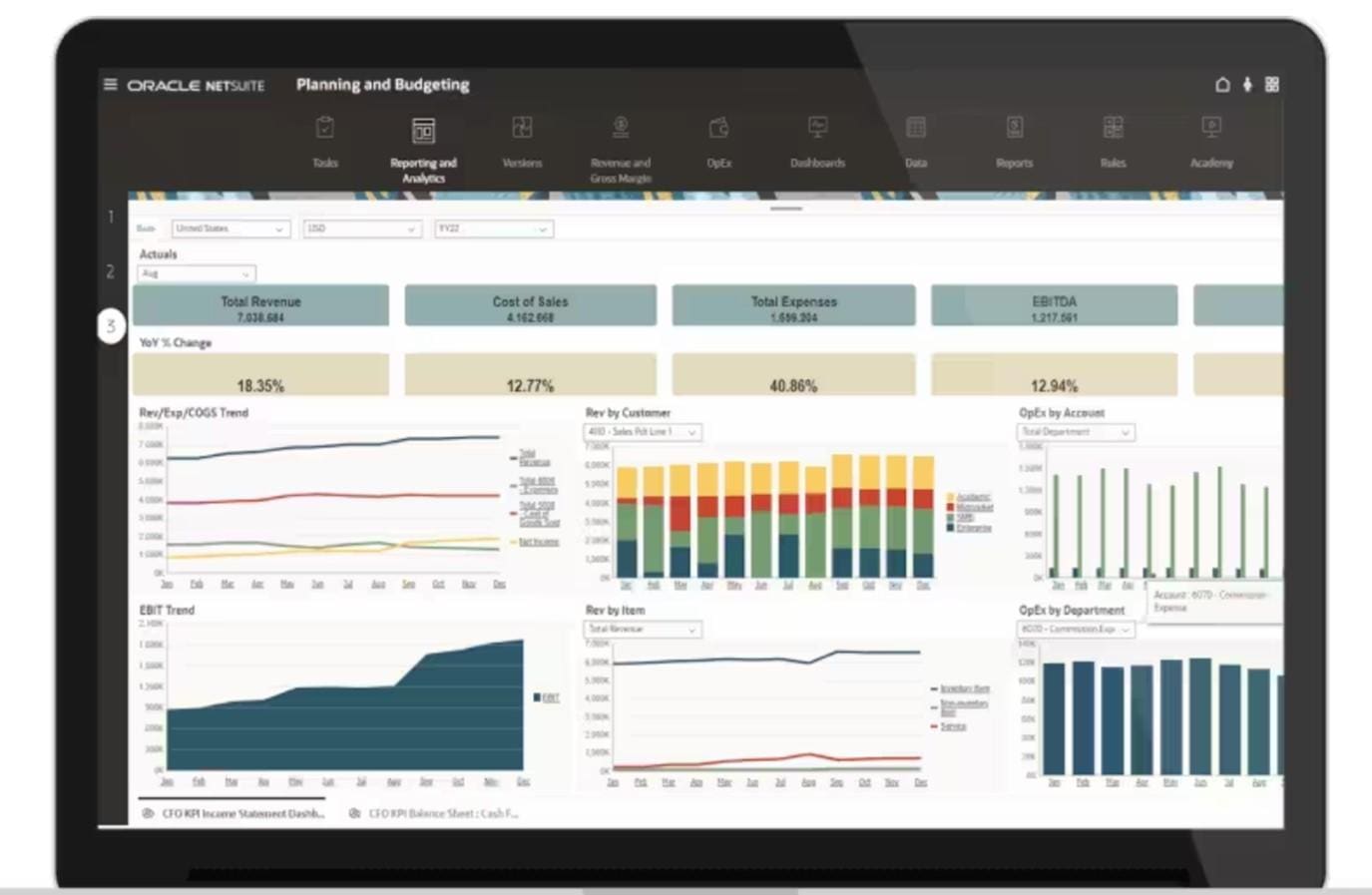
In one measure of EPM’s strategic value, Mordor Intelligence reported that the market for EPM software is expected to grow from $6.88 billion in 2023 to $10.83 billion in 2025. The market research firm attributes this nearly 10% cumulative annual growth rate to strategic factors, including businesses’ increasing need for data-driven decision-making, as they also seek to improve their focus on their core business to elevate performance. In addition to informing decision-making, EPM’s key strategic benefits include elevated capabilities to conduct scenario planning, align operational goals with strategic objectives and improve resource allocation and capital investment planning.
-
Data-Driven Decision-Making
Today’s business velocity and volatility require faster, better-informed decisions on everything from where to source components to how to satisfy customers. Unifying company information on a single platform and merging the operational and financial views of business activities position decision-makers to act quickly, but not simply shoot from the hip. Instead, for example, a retail executive considering a product launch amid mixed signals about the strength of the economy could review their company’s historical sales and cost data, but also keep a running tab on the price of raw materials, distribution costs and customer sentiment while analyzing different economic scenarios. Companies are building their capacity to make data-driven decisions like this, according to Forrester. In a survey by the market research firm, most respondents reported plans to increase spending in 2024 on the various components of EPM, such as customer analytics and tools for business intelligence and analysis, including AI.
AI further supports data-driven decision-making by recognizing patterns and suggesting alternatives using predictive analytics. Of course, the operative word is support, and a cautionary note from Gartner recently emphasized the importance of decision-makers’ own acumen. “Efforts to drive decision automation without considering the human role in decisions will result in a data-driven organization without conscience or consistent purpose,” said the market research group. Or, as a Harvard Business Magazine headline put it: “Data and Intuition: Good Decisions Need Both.”
-
Scenario Planning
Scenario planning can help businesses be more proactive versus reactive by visualizing potential risks and opportunities. In a worst-case scenario, this kind of planning can play out multiple outcomes, along with immediate crisis management steps. Similarly, best-case scenarios also need to be addressed, such as analyzing skyrocketing product sales and taking action to minimize stock-outs and maximize profits.
Techniques such as driver-based planning and rolling forecasts, described above, lay the foundation for scenario planning. That’s because they ensure that current business data is well understood and up to date. Then, EPM tools, such as planning and budgeting software, can run scenarios based on the input of changing variables for operating and capital expenditures, headcount costs, cash flow and other KPIs.
-
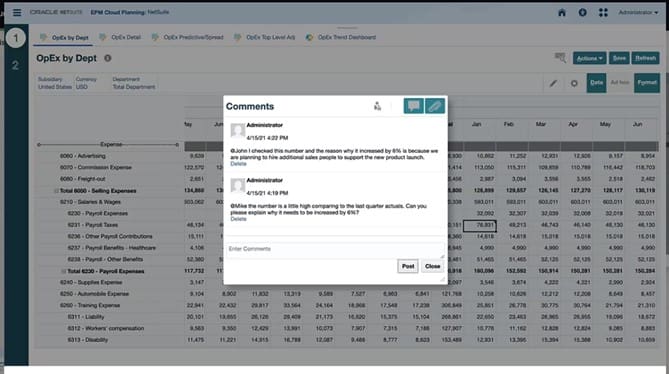
Aligning Operational Goals With Strategic Objectives
EPM’s role in catalyzing companywide collaboration to achieve shared goals ranks as one of its top strategic benefits. EPM can connect all stakeholders in a single environment. As it streamlines data collection, the information is visible to all, boosting engagement and accountability.
EPM dashboards make progress toward strategic objectives and operational goals clearly visible. Different departments and employees can also enter comments and assumptions for collaborative planning, budgeting and forecasting.
-
Resource Allocation and Capital Investment Planning
EPM can analyze the trade-offs of any given decision when allocating resources, always with an eye toward linking operations and finance with strategic goals. Scenario planning helps, as described above. What’s more, EPM tools can also analyze resource usage patterns to optimize allocations, for example, and time the investment of resources to avoid budget crunches.
As some of the biggest resource allocations, capital investments go to large-scale projects needing significant funding, such as the purchase of a new production facility or heavy equipment. Because of their size, these investments are analyzed, evaluated and prioritized with great care, thinking through their opportunity costs and the time value of money. EPM provides scenario planning and other tools to help business leaders objectively determine which capital projects to pursue and when. Then, as the facility begins operations or the equipment goes online, EPM software can track actual performance against projections, in terms of KPIs, such as cash outflows and inflows.
Technological Benefits of EPM
Technological advancements give decision-makers attributes that Silicon Valley promoters like to refer to as superpowers. Generative AI today tops the list of empowering innovations, but this technology stands on the shoulders of other game-changing advancements throughout the years, such as cloud computing and anywhere, anytime mobility. EPM gathers strength from all these and more. Its technological benefits include:
-
Integration With Advanced Analytics and AI
Advanced analytics delivers increasing levels of descriptive, diagnostic, predictive and prescriptive analysis of a company’s vast volumes of business data. AI’s predictive strengths are taking data analysis to the next level, as it’s increasingly used to monitor and analyze plans, forecasts and variances. EPM’s new AI capabilities are accelerating executives’ speed-to-decision by uncovering and highlighting trends, anomalies and correlations.
-
Cloud-Based EPM Solutions
Small and midsize businesses might not even get the opportunity to use EPM if not for cloud computing. The cloud enables critical aspects of the EPM model, such as the integration of data collection across departments, real-time access to continually updated information and closer collaboration between the finance team and other departments. The cloud’s inherently lower upfront costs and staffing requirements also make this technology a better fit for smaller companies. Gartner forecasts that by 2026, 75% of organizations of all sizes will be using cloud services as the basis for digitally transforming their business.
-
Mobile EPM Applications
Mobility enhances decision-making for executives on the go. Mobile EPM apps provide access to business information, such as checking KPIs, from anywhere. They also facilitate budget reviews and approvals as well as approvals of change requests in workflows. Some EPM software suites offer mobile apps that can send push notifications for urgent cost variances.
According to PwC, 73% of American companies have already adopted AI in some areas of their business, including 54% using generative AI. In the finance department, for instance, generative AI can help finance teams accelerate writing tasks, such as drafting summaries and narratives for financial reports. According to the Deloitte report, 87% of survey respondents said their companies have active AI applications, and these implementations are both generating revenue and saving costs.
Integrate Financial and Operational Planning With NetSuite EPM
NetSuite Enterprise Performance Management integrates planning, budgeting, forecasting, account reconciliation, financial close and reporting processes across the entire organization. This unified approach enhances the speed and accuracy of financial processes, while also providing business executives at every level of the company with the financial insights necessary for informed decision-making. Derived from the Oracle Fusion Cloud Enterprise Performance Management solution, NetSuite EPM ensures continuous access to the latest information by seamlessly integrating into the NetSuite ERP platform.
EPM makes maximum use of a company’s valuable business data to drive growth and profitability. It’s a best practice that is getting stronger every day in its ability to integrate, automate and streamline the aggregation and analysis of data for better decision-making. Cloud-based EPM puts these capabilities within reach of smaller companies whose challenges in coping with business pressures can be just as great — if not greater — as any large enterprise today.
EPM Benefits FAQs
How does EPM enhance financial planning and analysis?
Enterprise performance management (EPM) equips financial teams with accurate data, timely information, forward-looking analytics capabilities and inherent flexibility. Streamlining data collection across the company through an integrated cloud platform minimizes errors associated with manual data entry. The unified platform also ensures that information is accessible for collaboration among all stakeholders, even as departments automatically refresh data to accurately mirror the real-time state of the business.
Why is enterprise performance management important?
The speed and quality of decision-making needs to match the speed of change in business today, especially given economic volatility and digital era disruption. Enterprise performance management (EPM) equips company decision-makers with timely data as well as analytic capabilities to address challenges and opportunities as they unfold. EPM’s salient features include the integration of financial and operational data, combined with automation and analytics, to speed decision-making as it also streamlines routine financial procedures, such as the financial close.
How can organizations measure the ROI of their EPM investments?
Enterprise performance management (EPM) improves aspects of business, such as decision-making, collaboration and efficiency. Along the way, as EPM streamlines financial routines, its success could be measured in terms of reductions in the time taken to close the books, the ratio of journal entries that are manual, the percentage of financial statements requiring adjustments, the number of missed reporting deadlines, as well as improvements in other key performance indicators. Ultimately, the return on investment in EPM should be reflected in overall business performance.
What are the advantages of EPM software?
Enterprise performance management (EPM) achieves many of its benefits by automating and integrating operational data into financial planning, forecasting, budgeting, account reconciliation, financial close and reporting. With this unified view of company data, finance departments can benefit from enhanced budget accuracy, real-time forecasting adjustments, a streamlined financial closing process, compliance with regulatory requirements, the ability to identify profitable products/services and cost management.








