Expense management refers to the processes and policies that govern how employees are reimbursed for work-related spending. Travel outlays are often the first to come to mind when considering the process of submitting, approving, and processing expense reports, but modern expense management has a much broader scope. Remote work stipends, software subscriptions, client entertainment, and other expenses also need to be managed—and neglecting to do so can lead to compliance headaches and budget overruns.
What Is Expense Management?
Expense management is the end-to-end process in which organizations track, control, and reimburse employee spending. It includes everything from creating spending policies and approving expenses to auditing reports and managing integration with accounting systems. For both growing and enterprise-level companies, expense management plays a valuable role in maintaining financial oversight, making informed decisions about how business money is spent, and minimizing internal and external compliance risks.
Key Takeaways
- Expense management ensures employee spending aligns with company policy and goals.
- A clear, policy-driven process helps standardize how expenses are submitted, reviewed, and approved.
- Manual expense management is time-consuming and error-prone, while automation can speed up approvals, reduce errors, and improve compliance.
- When it comes to expense management software, scalability and flexibility are critical—especially for fast-growing businesses.
Expense Management Explained
Expense management means more than just tracking costs. It’s about creating a structured, policy-driven workflow that allows employees to use company funds for purchases that support business goals, all while verifying that every dollar is accounted for and compliant with company policies and accounting rules.
For example, say a marketing manager launches a regional campaign. In support, the team purchases a license for design software, runs targeted ads, and sponsors a local event. Each team member handles a different part of the spend. Larger, preapproved business expenses, such as the software license or event sponsorship, are paid with corporate cards, while smaller ad-hoc purchases, such as boosting a post on social media or buying printed materials for the event, are paid out of employees’ pockets and submitted for reimbursement. These employee-paid expenses are logged into the company’s expense management system, which routes the information to the appropriate approvers and flags any out-of-scope expenditures. Once approved, expenses are synced with the company’s financial management system to support cost tracking, budgeting, and reimbursement.
Marketing campaign spend is just one scenario. Expense management applies to a range of use cases, from the more obvious travel and entertainment (T&E) and client-facing activities to purchasing remote work equipment, departmental supplies, and other operating expenditures.
Spend Management vs. Expense Management
Expense management handles the day-to-day process of defining and enforcing policies, capturing receipts, and reimbursing employees. Spend management takes a broader view by categorizing and analyzing where money is going, discovering whether policies are effective, and adjusting them to ensure that they serve the business well. The two create a feedback loop: Accurate, timely expense data feeds better spend analysis, which, in turn, helps shape policies and budget strategies that can best support the business.
In the prior marketing campaign example, expense management is used to track, approve, and reimburse each purchase. Spend management looks beyond individual expenses to evaluate total campaign spend within the context of the overall marketing budget. The company might analyze the campaign’s return on investment to inform future adjustments—whether that means setting new spending caps, reallocating budgets, or refining approval thresholds.
The Expense Management Process
The expense management process is structured to verify that employee-initiated spend is properly submitted, reviewed, and reimbursed according to company policy. The typical workflow follows a variation of the following steps.
- Employee incurs expenses: An employee makes a business-related purchase, such as a meal, supplies, software, or travel tickets, using a company card or personal funds.
- Expense report is created: The employee logs into their company’s expense management system to create an expense report. Receipts are attached, along with any required details.
- Expense report is submitted: Once complete, the employee submits the expense report for review.
- Manager makes approvals: The company’s expense report system follows the company’s defined workflow. If managerial approval is required, the report is routed to the appropriate person. If it’s not approved, the report is returned to the employee for correction.
- Additional approvals are made: Some companies require further approvals if an expense surpasses a certain threshold, is made by a specific department, or is a particular type of purchase. This is usually relevant in enterprise environments with layered financial controls (requiring sign off from a finance director or VP, for instance).
- Report is audited: Some reports may be flagged for audit, either randomly or based on risk factors (e.g., spend thresholds or policy exceptions). Reports that fail review are returned to the employee for correction.
- Expense report is processed: Once all approvals are complete, the expense report is processed for reimbursement and recorded in the company’s financial system.
- Reimbursements are made: Employees are reimbursed for any out-of-pocket spending and receive notification. If a company card was used, no reimbursement is needed.
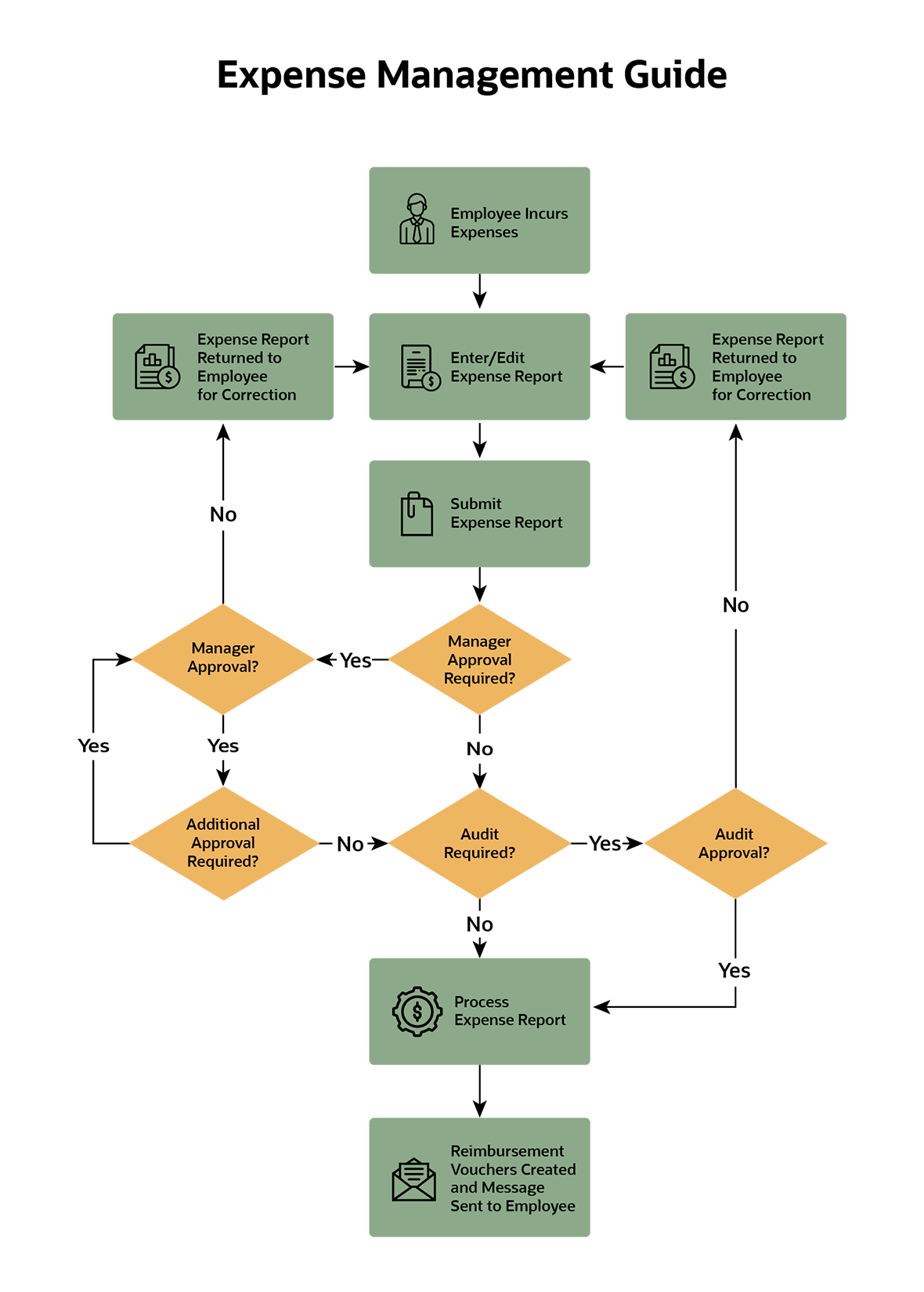
Source: Oracle(opens in new tab)
Benefits of Automated Expense Management Software
Automated expense management software can provide a wide range of benefits from both functional and organization perspectives. The following are some of the most common benefits experienced when automation is integrated into the expense management workflow:
- Saves time: From transaction to reconciliation, software can automate expense entry, approval routing, and reimbursement workflows.
- Saves money: Businesses can easily categorize spend and make adjustments—in real time, if necessary—helping to prevent budget overruns.
- Supports policy compliance: Employees are automatically alerted to policy violations before expense reports can be submitted, ensuring purchases stay within approved guidelines.
- Supports regulatory compliance: A centralized database of all expense claims supports easy access to historical data for internal and external audits.
- Improves data accuracy: Manual data-entry errors are minimized.
- Enhances employee experience: Intuitive mobile apps, faster reimbursements, and fewer manual tasks make life easier for employees.
- Scales with business growth: Companies can adapt approval workflows, expense categories, and controls as operations expand.
- Integrates with ERP and finance systems: Software that seamlessly integrates with enterprise resource planning (ERP) and finance systems support a smoother flow of data into accounts payable and the general ledger, reducing duplicate work and improving financial reporting.
Challenges of Manual Expense Management
Manual expense management can be time-consuming, prone to errors, and difficult to scale as a company grows and spending becomes less centralized. Common challenges include:
- Unclear or outdated policies: Ambiguous rules or poorly communicated policies can confuse employees, leading to inconsistent reporting and improper or inappropriate expense claims.
- Excessive time spent on approvals and corrections: Managers and finance teams might waste valuable time chasing receipts, clarifying vague submissions, and sending reports back for edits.
- Higher risk of errors and fraud: Manual data entry increases the chances of typos, lost receipts, and duplicate claims, while fraudulent submissions may be more likely to slip through unnoticed.
- Lack of real-time visibility: Without centralized tools, finance teams lack an up-to-date view of company spending, making it harder to manage cash flow, enforce and manage budgets, and identify problem areas.
- Difficult audit preparation: Manual systems may lack the ability to track and store proper documentation. This makes it harder to quickly provide complete, organized records during audits.
Automated Expense Management Features
Building internal expense management competency is crucial for small and midsize businesses—and automating expense management, which is often lower on the list of capabilities for which end-to-end automation is necessary, actually has a quick return on investment. Features to look for include:
- Mobile-app capabilities or a responsive UI that enables employees to easily track expenses where they most often occur—away from the desktop.
- Expense receipt management and GPS integration includes features such as optical character recognition that allow employees to take a picture of their receipts with a smartphone. The software maps to and automatically populates fields to streamline receipt tracking and report submission. With GPS integration, expense management software can automatically log and submit mileage.
- Corporate credit card integration eases or eliminates the process of collecting paper receipts from employees, as well as the process of reconciliation for the finance team.
- Customizable business rules streamline submission, approval, and payment and flag improper or questionable expenses before they are submitted to the next level for approval.
- Rule-based controls allow businesses to manage expenses proactively by setting enterprisewide policies and automating approvals. An auditable history makes it easy to provide auditors with necessary information for compliance with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX).
- Embedded analytics and dashboards allow businesses to analyze expense report trends, spot policy violations, and identify gaps in travel policies and potential areas of noncompliance. By breaking out expenses by category, policy violation type, and frequency, businesses can see top spenders, drill down to review detailed expense receipts, and uncover any expense policy violations. Expenses can be analyzed across cost centers, employees, and associated supervisory hierarchies.
- Integration with AP and/or payroll system enables a more seamless transaction-to-reconciliation-to payment process, meaning expense spend can be evaluated more easily as part of the company’s overall finances.
Why Use Expense Management Software?
The first-ever expense report, according to the Boston Business Journal, was likely submitted by Paul Revere. Following a series of rides in 1775, Revere submitted a handwritten receipt “to expense for self and horse during that time.”
Have your processes come much further than that? Of the 200 finance leaders surveyed for Center’s 2025 “Future of Mid-Market Travel & Expense” report, 50% say filling out expense reports remains a challenge. A core benefit of expense management software is that it reduces the time and effort required to submit, approve, and process employee expense reports; it also streamlines the process by which employees are reimbursed. In addition, software can help track and monitor how much and what employees are asking to be reimbursed for and make it easy to break out categories of spend. This helps reduce risk presented by fraudulent expense claims as well as better control spending companywide.
With expense management software, the business builds a database of information to mine for trends. Using this data, companies can quickly adjust expense management policies as the business climate demands.
Does Your Expense Management System Need to be Automated?
Excel is still a big part of expense management for many companies, and the resulting errors are a primary reason why businesses decide to automate their expense management. Following manual processes, employees submit their expenses on a spreadsheet and email the spreadsheet to someone to review. Then that person emails it to someone on the finance team who imports it into the financial management system.
It’s easy to see where mistakes and other inefficiencies can creep into expense reporting. Employees may lose or forget to include paper receipts or clearly define an expense. Managers waste time reviewing incomplete reports. Oftentimes, managers rely on the finance team to identify red flags, which wastes their time. And all of it delays the employee’s reimbursement and increases frustration and resentment of the whole process.
The risks of manual approval processes and the resultant errors extend beyond costs to the business internally. Businesses that need to comply with SOX demand robust reporting capabilities, but for tax compliance receipts must be logged and easily accessible. Strong governance provided by automated expense management processes is one of its most important features because their automated controls can stop mistakes and identify potential fraud.
How to Develop an Expense Management Policy
Here are a few tips to build an effective expense management policy.
- Define what is and isn’t covered: The latter category typically includes airline upgrades, child and pet care, house-sitting, commuting between the home and primary work location, and on-demand video in hotel rooms.
- Consider all of the ways an employee can leverage the expense management policy beyond business travel: This might include submitting charges for lower-cost subscription software tools and home office expenses.
- Decide how much to budget for travel and define limits for reimbursement: The Bureau of Transportation Statistics provides insights on average airfare. The U.S. GSA offers a calculator that shows allowances for lodging, meals and incidentals for federal employees based on location. And the IRS releases standard mileage reimbursement rates annually. Don’t forget to cover the relationship with suppliers and contractors in the expense policy.
How to Update an Existing Expense Management Policy
To ensure compliance, a company’s expense management policy needs to evolve with the environmental and economic conditions that employees are working under. Here’s a step-by-step approach for updating an existing policy.
- Monitor shifts in employee behavior and business environment: Pay attention to trends—increases in remote work, new regulations, changes in how employees incur expenses, etc. For example, during the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic, companies such as Google revised policies to address work-from-home spending and temporarily restricted certain expense categories.
- Analyze spending data to identify pressure points: Use real-time expense data to understand which categories drive spend and where policy adjustments may be needed, such as tightening limits on travel or clarifying remote work reimbursements.
- Establish a cross-functional expense policy team: Form a group of representatives from finance, HR, legal, sales, and other relevant departments. The team should meet regularly—ideally, monthly—to review spending trends, gather feedback, and propose updates.
- Approve and document policy updates: Revisions should be clear and specific. Focus on practical guidance, such as what is and isn’t allowed, so employees quickly get the gist. Update workflows in the expense management platform accordingly.
- Communicate updates: A multichannel approach can make sure the message gets through. Department-specific updates should be sent to managers, highlighting relevant changes. For major updates, a short training session or webcast may be necessary. Companywide memos from senior leaders should be sent to all relevant employees to explain why the policy is changing and how it affects them.
- Reinforce updates with examples: Anonymized real-world examples can help illustrate tricky policy areas, common mistakes, and how to avoid them. This can help make the changes relatable and more memorable.
- Centralize policy access: Updated policies and all supporting communication should be made highly visible and easy to access so companies can always find the most current version.
- Track acknowledgement: Ask employees to confirm they’ve read the updated policy, usually by signing off, to reinforce accountability and record compliance.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Even with the best communication, expense management fraud will happen in most companies. Some 13% of fraud schemes involve expense reimbursements, according to The Association of Certified Fraud Examiners’ “Occupational Fraud 2024” report(opens in new tab). Employees may try to pass personal expenses off as business ones. They may inflate expenses, make up expenses, or submit the same expense more than once.
One of the biggest mistakes companies make is failing to make it clear that policies apply to everyone—from staff and line workers to those who hold executive and upper management positions. Communicating the importance of policy adherence must come from the top.
Simplify and Automate Expense Management With NetSuite
NetSuite Expense Management helps companies simplify their end-to-end expense management process through automation. From submission and approval to posting and reimbursement, automated workflows enforce policy compliance and route approvals based on predefined policies. Employees can enter expenses via a web browser or mobile app, with the ability to upload receipt images while on the go. Expense data can then be directly integrated with project accounting, accounts payable, and the general ledger, helping organizations reduce manual data entry, improve accuracy, and keep up with spend in real time.
NetSuite also supports companies at every stage of growth. For global organizations, it offers multicurrency and multilanguage capabilities. For public companies—or those preparing to go public—it supports compliance with requirements, such as SOX. And as a cloud-based solution, NetSuite scales with the business to provide the flexibility needed to adapt to complex policies and evolving organizational needs.
Effective expense management involves far more than reimbursements. Rather, it hinges on creating a straightforward, policy-driven process that gives businesses control over spend. Automating that process with expense management software can help reduce errors, improve compliance, and free up time for more strategic work.









