Companies of all types and sizes must grapple with the challenge of staying competitive and meeting evolving customer demand. Service providers are especially sensitive to these pressures, as customer satisfaction is more public and readily available than ever before. After all, a subpar technician with a handful of bad reviews on an online site, social media account or search engine’s top page can drive away new customers and give a business a less-than-stellar reputation. But every industry has its own metrics to define a successful workday, such as jobs per day, closed tickets or hours in the field. Furthermore, a job’s expected time and cost can be hard to predict before a technical expert arrives at the site to fully diagnose the issue.
So, how can service providers be sure that their technicians, both in the office and on-site, are working effectively for their customers? To be sure, balancing workloads to meet customer needs without burning out technicians is a delicate act that requires careful planning and resource management. Luckily, service providers can use a simple metric to track how effectively their technicians are using their time and completing their work — technician productivity.
What Is Technician Productivity?
Technician productivity refers to the effectiveness with which technicians complete their tasks and responsibilities. Technicians include on-site staff, such as auto mechanics, and field service workers, such as appliance repair experts. Their productivity is a measure of how effectively they use their time and effort to create tangible results, such as completed service calls, repairs or installations. Productive technicians prioritize the best use of their time and talents to serve customers, ultimately impacting a company’s ability to meet demand and maintain profitability.
Maximizing technician productivity is especially important for small and medium-size businesses with limited resources. Overall, worker productivity has continued to rise over time, according to St. Louis Fed data. By increasing productivity levels among technicians, businesses can take on more jobs and projects without hiring more staff or hurting customer satisfaction. Business leaders can also track productivity to identify areas to improve workflows and more strategically allocate resources and labor, ultimately driving growth without compromising service quality.
Key Takeaways
- Technician productivity is a crucial metric for service providers. It impacts their ability to meet demand and deliver quality service in a timely manner.
- Productivity and efficiency are separate but similar metrics for assessing technician performance. These, alongside other key performance indicators, paint a fuller picture of technicians’ work and their effect on overall profitability.
- Regular monitoring and analysis of technician productivity can lead to significant operational improvements, including better allocation of resources and labor, enhanced service quality and reduced operational costs.
Technician Productivity Explained
Technician productivity is about more than the speed at which technicians work; it also considers the quality and consistency of their output. A technician may finish a job quickly, for example, but if they have to go back to the customer and redo rushed work, it likely wasn’t a productive use of their time. Businesses use productivity in conjunction with other key performance indicators (KPIs), such as first-time fix rate and mean time to repair, to assess how effectively, in both time and quality, technicians are completing their tasks. By tracking this data over time, often through business software with data analytics capabilities, business leaders can spot trends and make informed decisions about staffing, training, tools and technology investments.
To avoid outliers and misleading data, managers typically look at productivity metrics as averages over time, rather than as single shifts or isolated services. For example, managers can use technician productivity metrics to determine the optimal number of service calls to assign a technician in a day without compromising service quality. But an atypical or especially difficult service call may take hours longer than expected, significantly skewing a normally high-performing service technician’s productivity. These events should be flagged and factored into individual or team performance levels to more accurately identify which workers are struggling and need assistance and which jobs will require additional time or resources in the future. This detail-oriented approach fosters a culture of continual improvement as the business grows, building a more dynamic and responsive service operation that addresses customers’ needs without overworking employees.
Technician Productivity vs. Efficiency
Technician productivity and efficiency, while related, are distinct metrics that businesses use to gauge performance. Productivity measures the percentage of hours an employee actively works relative to their total hours clocked in. Efficiency, on the other hand, measures active work hours relative to the number of hours billed to customers. Under most circumstances, including hourly employment, productivity will not exceed 100%, as that would require technicians to work longer hours than they were present for. But if the company bills customers for jobs based on average, flat or industry standard hours, technicians may complete the job in fewer hours than will be billed. This creates a greater than 100% efficiency rate and allows technicians to move on to other projects, creating more billable hours than their total shift. Finishing early also allows staff to work on nonbillable tasks, such as taking test drives, cleaning workspaces or running quality checks, without incurring losses for the company.
By enhancing efficiency, companies can increase their billable hours without expanding their staff. However, it is important to compare rates and prices to those of competitors and to remain transparent with customers, as they won’t want to pay more for jobs that were overestimated and, therefore, overcharged. Additionally, even highly skilled and efficient workers can make mistakes, especially when rushing, so businesses should employ quality checks before signing off on completed projects. As with productivity, efficiency should be treated as a careful balancing act to maximize billable hours without sacrificing quality or worker satisfaction.
How to Measure Technician Productivity
Calculating technician productivity requires only two values: the hours the technician spent actively working and the total hours that they were clocked in. The formula to calculate productivity as a percentage is straightforward:
Technician productivity = [(Hours spent working) / (Hours clocked in)] x 100
For example, say a technician completed three jobs today, each taking two hours, but was clocked in for a total of eight hours. Their productivity would be calculated as follows:
Technician productivity = (6 hours worked / 8 hours clocked in) x 100 = 75%
This means that for the duration of this shift, 75% of the worker’s time was spent on productive work, while the remaining 25% was spent elsewhere, such as on breaks, administrative/miscellaneous tasks or downtime.
Service managers use this calculation to identify areas where workflow improvements can be made, ensuring that technicians are allocated enough work and resources to minimize idle time without affecting their well-being or performance. However, every industry is different, and some may have higher expected levels of productivity than others. For instance, a field technician servicing clients located hours apart will spend more time driving than a mechanic working on cars in a centralized garage. Managers should consider these differences when determining what is considered active work and what isn’t.
However a business determines productivity, regularly monitoring and tracking technician productivity over time can inform operational improvements. Even small improvements to productivity, such as buying an extra set of tools to minimize repeated travel from one side of the shop to the other, can significantly influence the pace of work and customer satisfaction.
Benefits of Tracking Technician Productivity
Tracking technician productivity is a strategy for identifying inefficiencies and revealing untapped opportunities for improvement and growth. Here are a dozen ways analyzing technician productivity can benefit businesses.
- Identifies efficiency gaps: Businesses can compare productivity metrics for different workers or tasks to quickly identify areas where processes aren’t as efficient as they could be. This helps managers target their improvements where they would do the most good and ensure that resources are allocated in a way that effectively optimizes every aspect of the service.
- Streamlines workflow: Productivity data helps decision-makers identify tasks that can be improved, automated or eliminated, such as manual paperwork filing or repeat data entry. This workflow streamlining reduces errors and simplifies technicians’ jobs, while also speeding up service delivery.
- Optimizes technician deployment: Understanding productivity levels enables businesses to deploy their technicians more strategically. By matching the right technician with the right job on the basis of skills, location and availability, companies maximize their workforce’s effectiveness and minimize downtime. For example, once a technician is deployed, managers can check whether there are any other jobs in the area that the technician is qualified for, such as proactive maintenance, to prevent a second technician having to make the trip during a later shift.
- Balances workloads: Tracking productivity ensures that workloads are evenly distributed among technicians to prevent burnout and guarantee that no single technician becomes overwhelmed. If employees show significant fluctuations in productivity, it might be because they aren’t assigned to the jobs best suited for their skills, and they may require additional training or assistance to maintain standards of quality.
- Improves response times: With a clear view of productivity, businesses can better manage their service schedules and more effectively leverage their staff to improve response times. Faster service boosts customer satisfaction and helps service providers stand out in competitive markets where quick turnaround is demanded by customers, such as plumbing or electrical work.
- Increases first-time fix rates: Productivity data can highlight trends and patterns in service calls, helping businesses identify areas where technicians may need additional training or resources before arriving at the service location. It can also enhance proactive maintenance through better scheduling and deployment, giving technicians more detailed data about what tools to bring and what services to perform when they’re called. This can significantly increase first-time fix rates, reducing costs and the need for follow-up visits, as well as enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Guides investment in tools and technology: Business leaders can use productivity metrics to inform investment decisions when implementing new tools. This data provides managers with a road map of inefficient areas or service workflows that can be enhanced by new technologies. Managers can then make investments that focus on service areas with the greatest potential return in both quality and financial measures.
- Reduces operational costs: By boosting productivity, businesses can reduce their operational costs to strengthen their bottom line. Through more efficient workflows and resource allocation, managers can lower their overhead expenses and trim waste. For example, an appliance repair company can track productivity for various repairs to identify gaps in technician training programs, which, when improved, will reduce the time, labor and resources required to make these repairs. Over time, these improvements can build a more sustainable, long-term operation.
- Boosts revenue opportunities: Improved productivity opens new revenue opportunities by empowering businesses to offer faster service times and higher first-time fix rates. Through high-quality expertise and proven results, service technicians can outperform their competition to drive repeat business and referrals.
- Identifies achievements and areas for growth: Productivity metrics allow businesses to track an individual employee’s performance and compare it to other team members’ output and established benchmarks. This information lets managers recognize and reward high-performing technicians to motivate employees and, potentially, boost morale. It’s important to remember, however, that technicians with complex tasks can experience underlying and unavoidable complications that may also be worthy of praise and recognition, even if they seem to hinder productivity metrics.
- Facilitates strategic planning: Productivity data helps business leaders understand what factors are affecting productivity and the impact they’re having. This understanding allows managers to create more accurate performance and revenue forecasts and develop strategies to reach those targets.
- Enables competitive benchmarking: By calculating productivity as a percentage, businesses can compare performance against industry standards and internal benchmarks, regardless of total hours, workers, services or other variables. This direct comparison helps businesses identify their strengths and weaknesses relative to other players in the industry and strategic goals, spotlighting areas where they can distinguish themselves and gain advantages or make improvements.
5 Strategies to Improve Technician Productivity
As industries evolve and customer expectations rise, companies must adopt strategic measures to ensure that their technicians are equipped with the latest technologies and best practices. The following five strategies directly address how technicians across various sectors can overcome common productivity challenges to improve performance, reduce downtime and increase profitability.
1. Time Management and Prioritization
To manage how technicians can optimally use their time, businesses should establish clear, measurable metrics that both workers and management can reference to monitor performance and ensure that everyone is on track to meet their goals. These metrics typically include general productivity but can also focus on more industry-specific KPIs, such as jobs completed or number of clients serviced in a given time period. By prioritizing critical and time-sensitive work, technicians know they’re using their time and resources effectively, thereby reducing operational costs and downtime while having the largest possible impact on overall success. As new tasks are added to workflows, businesses must regularly reassess priorities, emphasizing agility and responsiveness to maintain or expand customer satisfaction and all competitive advantages.
2. Training and Skills Development
By investing in comprehensive training programs, businesses can be sure that their technicians are equipped with up-to-date skills and the knowledge to handle their tasks. This training not only expands technicians’ ability to complete complex jobs and projects — creating new revenue opportunities — but also significantly ramps up the quality and speed of tasks, directly increasing day-to-day productivity. Well-trained technicians are less likely to make errors that feed customer frustration and the need for rework. Ongoing investments in workforce development can continue to earn investment returns as the business grows and more customers learn of the business’s high-quality expertise. Additionally, regular training and assessment can give managers insights into technicians’ untapped skills and potential when creating new positions or promoting staff.
3. Leveraging Technology and Automation
Modern service providers can access a variety of sophisticated technologies, especially those with built-in automation capabilities, to expedite processing times, minimize human error and enable continuous operations, even beyond standard working hours. Automation accelerates data collection and processing, freeing technicians from repetitive and time-consuming tasks, such as generating reports, analyzing spec sheets, updating customers with progress notes, and more. Technicians can then focus on more complex, value-adding activities or customer-focused problem-solving that drives innovation and gives customers a more hands-on and responsive experience. Many of these tools are integrated into larger business solutions, such as an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, to provide business leaders with organization-wide productivity metrics from one centralized location. Leaders can leverage this increased visibility to spot weaknesses and take proactive steps to increase productivity, rather than waiting for customer complaints or lagging employee reports.
4. Improving Communication and Collaboration
Upper management, direct supervisors and technicians need to openly communicate and collaborate to create a realistic view of productivity and develop strategies to improve it. Technicians working for the same company may have different views on what defines productive time, and everyone needs to be on the same page when improving performance. For example, technicians who build and test devices in the office will likely need to consider workstation cleanup and cataloging inventory when calculating overall productivity calculations. Service providers in the field, on the other hand, may spend more time traveling and directly interacting with customers, and their productivity metrics and goals should reflect these responsibilities. Therefore, when developing performance metrics, managers should collaborate with their technicians to accurately reflect the jobs and projects that each one is responsible for. This cohesive team effort helps align each worker’s job with overall company strategies, creating a more streamlined, agile and effective way to measure productivity. Additionally, open communication among peers can help technicians share best practices and innovative solutions for day-to-day work, contributing to a more productive and safer work environment for staff at all levels.
5. Workflow Optimization
Managers can optimize their workflows by mapping out the sequence of tasks required to complete a project, identifying inefficiencies and redundancies along the way. These streamlined workflows equip technicians with all the right information and tools they need, without wasting resources or cluttering workstations and company vehicles. This focus on process efficiency enhances the capacity for technicians to handle a greater volume of service requests without harming the customer experience. This should be an ongoing process, rather than a one-and-done assessment, as new technologies, best practices and even employee skill sets are discovered and implemented. Through continuous improvement, companies can improve service delivery speed, reduce operational and material costs and deliver more appropriate and timely services.
Industries That Measure Technician Productivity
While managers can nearly universally apply the core concepts of productivity to their technicians’ work, how they measure, value and improve productivity can vary significantly from one industry to another. These nuances are caused by differences in specific demands, tools and customer expectations for particular sectors, including automotive, manufacturing, HVAC and field service, and are explored in greater detail below.
Automotive Service and Repair
Automotive service and repair technicians typically measure their productivity as the ratio of active work hours to total hours. This metric is crucial because it directly correlates with the shop’s ability to quickly complete jobs and return vehicles, an important factor when customers are choosing where to bring their business. Automotive shops strive to maximize these ratios by reducing nonproductive time and making sure technicians have the necessary skills, tools and information to perform tasks efficiently. This includes balancing spare-part inventories with procurement and storage costs, as waiting for relevant part delivery is a primary cause of downtime. To be sure the right parts are ordered and used as soon as they’re received, many shops emphasize training and equipping technicians with advanced diagnostic tools. These tools also help improve first-time fix rates and limit the need for costly repeat visits.
Manufacturing and Industrial Services
For manufacturers and other industrial services, productivity is closely tied to the maintenance and uptime of production equipment and can vary significantly based on the quality and depth of a business’s equipment maintenance schedule. For example, a factory with a robust predictive and preventive maintenance schedule may have technicians completing quick checks and minor repairs, jumping from job to job throughout the day. Another factory with older, less reliable equipment may primarily dispatch technicians for major and time-consuming repairs. Realistically, most businesses will require a mix of the two, as productivity directly impacts business slowdowns or stoppage when machinery goes offline for repairs, even for a short period. According to St. Louis Fed data, manufacturing productivity has remained relatively stable from 2014 to 2024 (aside from the since-recovered dip during the COVID-19 pandemic), opening opportunities for innovative manufacturers to pull ahead of the competition. By increasing productivity and prioritizing preventive maintenance, often aided in real-time by artificial intelligence and Internet of Things devices, businesses can get operations back up faster, increasing output and minimizing losses.
HVAC (Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning)
Technicians in the HVAC industry maintain HVAC systems in both residential and commercial settings. HVAC productivity metrics typically include the number of service calls completed per day and how quickly technicians diagnose and resolve issues. Additionally, due to the seasonal nature of customers’ HVAC needs, especially in regions with extreme weather conditions, HVAC companies often focus on rapid response times and effective issue resolution to ensure customer comfort and safety, even in high-volume periods and urgent situations. Modern technicians can enhance their response times by leveraging real-time mobile technology to remotely and efficiently access all relevant technical information from job sites, rather than relying on cumbersome manuals or calls to the office.
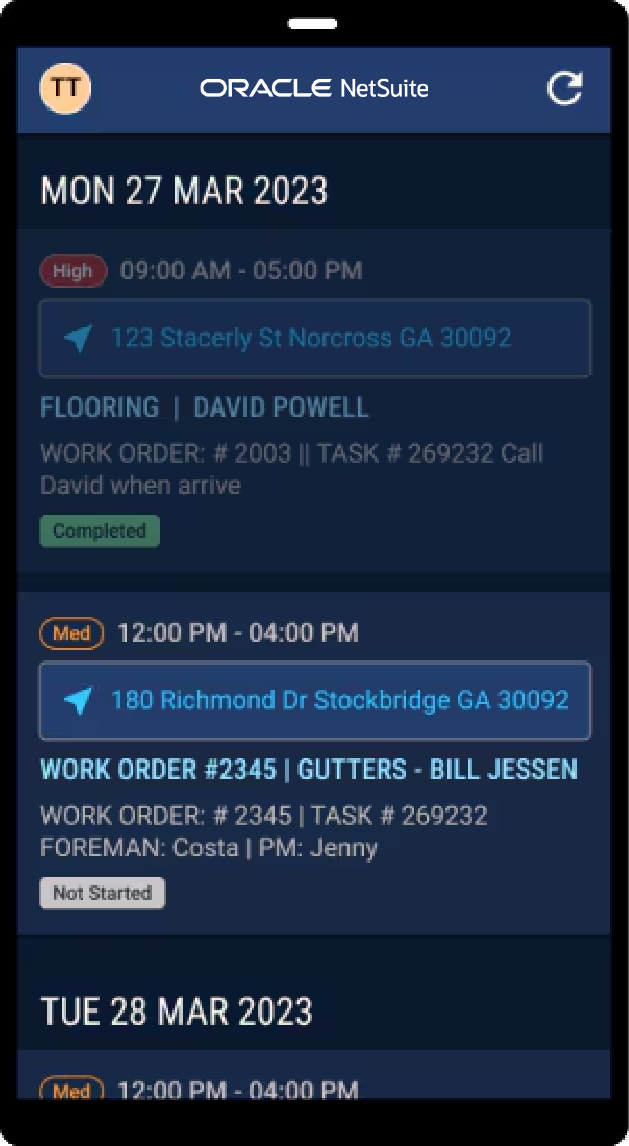
Field Services
Field services cover a broad range of industries, from telecommunications to utilities, and involve off-site technicians installing, maintaining and/or repairing equipment and infrastructure. Productivity for technicians in the field is heavily influenced by travel time, scheduling efficiency and first-visit repairs. For modern technicians, technological advancements play a significant role in maximizing productive work time. Some of this technology includes GPS for optimal routing, automated data entry and report generation software and mobile applications for real-time communication between technicians and the office. These tools can also help technicians keep customers informed of any changes and estimated arrival/completion times, improving upon the broad estimates and guesswork that commonly frustrate customers.
How to Automate Technician Productivity Tracking
By automating how they track technician productivity, businesses can gain more detailed, accurate and up-to-date information on technicians’ performance when serving customers. Mobile and cloud-based software solutions automatically track work hours, job progress, overall efficiency and other customizable metrics anytime, anywhere. Automated reports can even be generated in the middle of a project, without interrupting the technician’s work with time-consuming manual activity logs. For instance, mobile applications allow technicians to easily clock in and out of individual jobs directly from the job site to automatically calculate productivity based on the time spent on each task as opposed to the hours clocked in. This immediate visibility helps managers update project expectations and identify areas where improvements can be made to speed up workflows and create more accurate schedules.
Automated reporting tools can also run prebuilt and customized reports to analyze productivity and establish trends over time. These trends can justify productivity goals, training decisions and personalized development plans for technicians at any level. Business leaders often integrate these automation tools with other existing business systems, such as customer relationship management, inventory management, accounting and ERP software, to create a cohesive ecosystem that supports data-driven decision-making.
Measure and Improve Technician Productivity With NetSuite
Business leaders can’t truly optimize their technicians’ productivity without a detailed understanding of each technician’s strengths and weaknesses. With NetSuite Field Service Management, companies gain real-time insights into job and technician status, improving decision-making and resource allocation. NetSuite’s all-in-one platform leverages automation to collect and organize data throughout operations, enabling business leaders to manage operational costs more effectively, reduce wasted labor hours and optimize inventory levels.
NetSuite’s cloud-based platform also has full mobile app functionality that field technicians can use on the go to securely access essential information and customer history whenever and wherever they need it. Furthermore, NetSuite provides detailed analytics that can help businesses understand the profitability of each job, customer and service contract, as well as plan proactive maintenance and repairs. This comprehensive view of operations creates a more dynamic, responsive and profitable service operation.
Measuring and improving technician productivity is an important endeavor that can significantly influence a service provider’s success. By implementing key strategies, such as time management, skills development and technology integration, businesses can optimize their workforce’s time and labor to foster growth. But to identify areas for improvement and assess the impact of new strategies, businesses need transparency into their technicians’ work. Through more comprehensive productivity tools, often integrated into larger business software with automated capabilities, managers and business leaders can determine where strategies are enhancing the customer experience and reducing costs, and where technicians need more help. Every productivity improvement, no matter how small, helps create a more effective and competitive team of technicians that are better prepared to serve customers.
Technician Productivity FAQs
How do you calculate productivity of a technician?
Technician productivity is calculated by dividing the number of hours the technician actively works by the total number of hours in their shift and then multiplying by 100. For example, if a mechanic works on cars for four hours out of a five-hour shift, their productivity rate is 80%.
What is the difference between technician productivity and efficiency?
Technician productivity shows how effectively a technician uses their time to complete tasks. Efficiency, on the other hand, assesses how quickly a technician can complete a job, compared to the estimated allotted time. High efficiency reflects a technician’s skill and speed relative to industry standards or averages.
How do you track technician efficiency?
Technician efficiency can be tracked by dividing the number of hours a technician bills for a job by the actual hours they spend completing it, then multiplying by 100. For instance, if a shop bills one hour for a diagnostic test but the technician completes it in half an hour, their efficiency rate would be 200% [(1/.5) x 100].
What is productivity in a service department?
Productivity in a service department refers to the percentage of available time used for active, billable work. This measure reflects both technicians’ output and the service department’s ability to generate and manage work orders. High productivity percentages indicate greater profitability for the service department and can free up staff for non-billable activities, such as workstation organizing or breaks, without incurring losses.









