Millions of invoices are exchanged between sellers and buyers every day — yet sending and processing invoices traditionally has involved labor-intensive and error-prone manual procedures. Electronic invoicing offers an alternative. Managing invoices electronically enables organizations to streamline this universal business function. With e-invoicing, suppliers can automatically generate and send invoices to customers in a structured digital format, and customers can automate the processing and payment of those invoices. The benefits include increased efficiency, fewer errors and shorter payment cycles.
What Is Electronic Invoicing (E-Invoicing)?
An e-invoice is a digital invoice containing billing information presented in a structured format that is transmitted electronically from supplier to customer. E-invoicing offers considerable advantages for both sellers and their customers. Businesses supplying products and services can automatically generate e-invoices from sales transactions, instead of having to create and print them manually. Companies that receive e-invoices from their suppliers can automate labor-intensive processing steps, such as three-way matching of invoices to purchase orders and shipments.
Key Takeaways
- E-invoicing involves creating and sending digital invoices in a structured format that enables automated invoice processing.
- E-invoices can be automatically generated and processed by accounting software or ERP solutions.
- Benefits of e-invoicing include reduced manual effort, fewer errors, faster invoice processing and improved cash flow.
Electronic Invoicing Explained
Electronic invoicing can eliminate time-consuming, error-prone and costly manual invoicing procedures. Traditionally, employees have created invoices by hand, then either stuffed them into envelopes and mailed them to customers or emailed them as PDF images. This is a labor-intensive process that’s prone to data-entry errors. Customers then perform the similarly labor-intensive processes of manually checking invoices against their purchasing records and the shipments they received before paying them, often by check. E-invoicing enables businesses to automate accounts payable processes while simultaneously allowing customers to automate accounts receivable processes, especially when e-invoicing functions are integrated into their business applications.
Although adoption of e-invoicing has grown rapidly in recent years, its roots can be traced as far back as the 1960s, when businesses began using pre-internet electronic data interchange (EDI) networks and data formats to exchange invoices and other business information. (The technology is still widely used in some industries.) Many e-invoicing systems now use more modern, cloud-based platforms and XML formats to exchange invoices.
Video: What Is E-Invoicing?
How Does E-Invoicing Work?
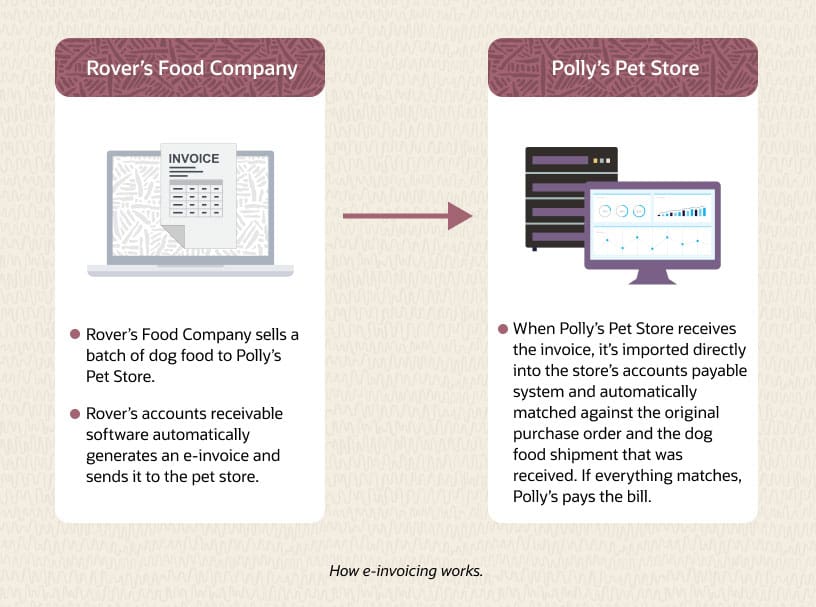
Businesses derive the greatest benefit from e-invoicing when it’s integrated into their accounting or enterprise resource planning (ERP) software. This integration enables companies to automate many or even all invoice processing steps. Let’s say a company typically invoices customers once it has shipped their orders. The ERP system can automatically generate and send an invoice at that point without requiring any additional data entry, using the information in the customer order. Because those invoices are in a structured digital format, customers that receive invoices can directly import them into their business applications. The customer’s business software can then automate the processing of the invoice, including the critical steps of matching the information in the invoice to the original purchase order and to the goods received. If everything matches, the customer pays the invoice.
Invoice Types
Invoices can be categorized according to their business use. Here are some of the most common types:
-
Sales invoice.
This is the most common type of invoice. A business creates a sales invoice to request payment when it sells goods or services to a customer. Standard information on the invoice includes supplier’s and customer’s names and contact information, invoice number, the good or service provided, amount owed, payment deadline and payment methods accepted.
-
Pro forma invoice.
Used by sellers to provide an estimate before issuing any goods or services, this type of invoice contains the estimated cost, a description of the work and any other information the customer may need to decide whether to go ahead and place an order.
-
Past-due invoice.
This is sent to a customer that hasn’t paid a sales invoice by the due date. It may include late fees specified in the sales contract. It should be sent to the customer as soon as possible after the due date and include all the details that were on the original sales invoice.
-
Credit memo.
A business sends a credit memo, also known as a credit invoice, when it needs to provide a discount or refund. A credit invoice might be issued if a product was damaged during shipping or to correct a previous invoicing error.
-
Debit memo.
Also called a debit invoice, this document indicates that the business needs to increase the amount owed by the customer. For example, a business might issue a debit invoice if the original amount billed for a project was an estimate and it used more time and resources than originally anticipated.
-
Mixed invoice.
This kind of invoice combines credit and debit charges into one invoice. The net amount reflects what the customer owes.
-
Commercial invoice.
This is a specialized type of invoice required for some international transactions. It is used to obtain customs clearance and calculate any tariffs and duties. Depending on the country involved, it may include the customs classification of the goods, as well as the quantity, weight or volume, description and price.
-
Timesheet invoice.
Businesses that bill for their services on an hourly or daily basis typically send timesheet invoices. A timesheet invoice includes the number of hours worked and the hourly rate charged. Professionals who use timesheet invoices include lawyers, consultants and psychologists.
-
Interim invoice.
Large projects are often completed in stages, with partial payments made when milestones are reached. The milestones and payments are agreed upon before the project begins. Interim invoices help small businesses manage their cash flow on large projects.
-
Final invoice.
This is sent at the completion of a large project. It details the amount owed after deducting any interim payments from the total project cost.
-
Recurring invoice.
Businesses that provide continuous or repeating services often use recurring invoices, which are issued monthly or at other regular intervals. Examples of businesses that issue recurring invoices include companies that provide cloud-based software, streaming services or gym memberships.
Manual Invoicing Challenges Solved by E-Invoicing
Employees have been manually processing invoices for hundreds of years — and employers have been coping with the challenges of manual processing for just as long. Here are some of the most common drawbacks:
-
Unforced errors.
Humans make mistakes, so data-entry errors are almost inevitable when manually creating invoices. Errors annoy customers, can potentially result in lost revenue and take time and energy to fix.
-
Impaired productivity.
Manual invoice processing is time-consuming not only for suppliers but also their customers, who must spend a considerable amount of time manually checking every invoice against the associated purchase orders and goods receipts.
-
Higher costs.
Having to print and mail invoices adds expenses for envelopes and postage, plus the cost of the employee time required.
-
Risks of fraud and duplicated payments.
When invoices are created manually, instead of generated directly from transactions, there’s a greater potential for duplicated, inflated or fake invoices.
-
Payment delays.
Manual processes can result in slower bill payment. For suppliers, the delay negatively impacts cash flow. For customers, it can mean missing out on early-payment discounts.
9 Developments Shaping the Future of Accounting

Benefits of E-Invoicing
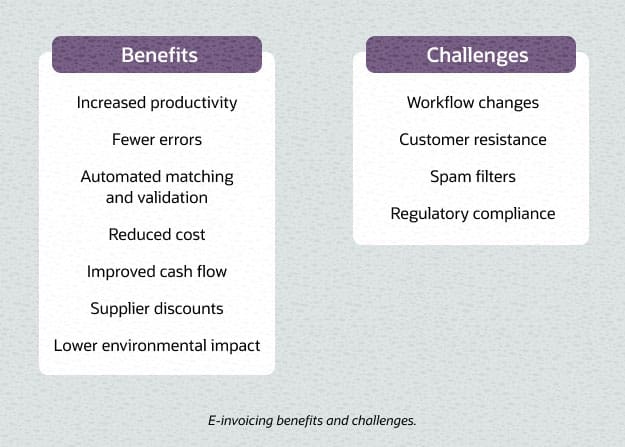
E-invoicing can provide a wide range of business benefits, from lower costs to fewer errors and improved cash flow. Many of these benefits stem from the fact that e-invoicing facilitates broader automation of accounting and payment processes for both suppliers and customers. Benefits include:
-
Increased productivity.
E-invoicing greatly reduces the need for manual effort for suppliers. Employees don’t need to spend time entering data because ERP systems automatically generate and send e-invoices when sales transactions are recorded or products ship to customers. This frees employees to spend more time on higher-level activities.
-
Fewer errors.
Transaction data is automatically copied to e-invoices, eliminating the potential for data-entry mistakes. This also reduces the likelihood of time-consuming and frustrating payment disputes.
-
Automated matching and validation.
For customers, e-invoicing simplifies the automated matching of invoices against purchasing and shipping documents (three-way matching) to ensure that the invoice accurately reflects what was ordered and received. This can save an enormous amount of effort. Suppliers can more easily reconcile the payments received against the original sales transactions.
-
Reduced cost.
Reduced manual effort and greater accuracy translate into lower costs for both suppliers and customers.
-
Improved cash flow.
E-invoicing can dramatically shorten payment cycles, improving cash flow for suppliers. Automation helps ensure that suppliers can send invoices promptly, meaning that customers may pay faster because they can quickly validate the invoices they receive.
-
Supplier discounts.
Many suppliers offer discounts for fast payment — and impose penalties when payments are late. E-invoicing can make it easier for customers to pay quickly and enjoy supplier early-payment incentives.
-
Less environmental impact.
E-invoicing eliminates paper, ink and envelopes from the invoicing process, reducing their environmental impact.
Challenges of E-Invoicing
Though e-invoicing has many benefits, it’s also important to be aware of potential obstacles to implementation. Switching to e-invoicing may involve changes to companies’ internal processes and the way they interact with their customers and suppliers. In some regions, there are also compliance considerations. Here are some of the potential challenges:
-
Workflow changes.
E-invoicing can transform accounts receivable and accounts payable processes. Although the changes can make employees’ lives easier, some people may not like the idea of forgoing familiar, long-standing procedures. It’s important to educate them in advance.
-
Customer resistance.
Not all customers may be able to take full advantage of e-invoicing. Some may not even be accustomed to receiving invoices via email. Some countries require customers to give their consent before suppliers can send them e-invoices.
-
Spam filters.
If e-invoices are sent via email, they may wind up in customers’ spam folders. This can be avoided by having a customer portal where invoices are delivered and customers can be notified.
-
Regulatory compliance.
Many countries require companies to use specific e-invoicing formats and networks when doing business with public-sector organizations and, in some cases, even when transacting with other businesses. Other common requirements include digital signatures, automated tax reporting and storing e-invoices for a specific length of time.
E-Invoicing Standards
E-invoicing standards define sets of invoice types, formats and syntax with the goal of enabling businesses to exchange and automatically process invoices and other business documents. In many countries, companies must comply with e-invoicing standards to do business with government agencies; some countries mandate that businesses use e-invoicing standards even for transactions with other businesses. Many standards exist. Here are some of the more common ones:
-
Universal Business Language (UBL)
is a set of standards for XML-based business documents that has been adopted by the International Standards Organization. The Federal Reserve, together with an industry group, is developing a pilot project based on UBL for a standardized B2B (business-to-business) electronic invoice exchange system in the U.S. -
Peppol
is a network and set of specifications for exchanging business documents that’s used by many European countries. It has also been adopted by other nations, including Australia and Singapore. -
American National Standards Institute (ANSI) X12
is an organization develops standards for supply chain messages transmitted over EDI, including a standard invoice that sellers can use to request payment for goods and services. Subsets of X12 standards have been developed for use within the retail, oil and gas, electronics, automotive and other industries. -
Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce and Transport (EDIFACT)
is an international standard developed by the United Nations. It includes a set of standard messages for exchanging business documents. It’s widely used by big companies in the U.S. and in Europe.
How to Create E-Invoices
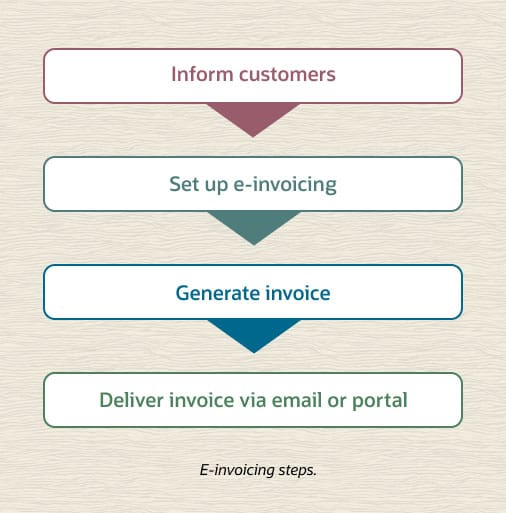
The details of creating e-invoices vary, depending on the software you choose (more on that, below). However, the basic steps will be similar:
-
Inform customers.
Before starting to send customers e-invoices, make sure they’re willing and able to receive them. In some countries, you may need their written consent. If you’ll be emailing invoices to them, make sure you have the correct email address.
-
Set up e-invoicing.
Advanced accounting software allows businesses to set up automated invoicing and customize invoice templates for unique customer needs. Ensure that your e-invoice format includes all the information necessary to identify the transaction, supplier and customer, and other details, such as acceptable payment methods and any applicable taxes or discounts.
-
Generate the invoice.
Ideally, your accounting software will automatically generate e-invoices from sales orders, including any taxes or customer discounts
-
Deliver the invoice.
Send the e-invoice to customers via email or through a secure portal.
Choosing an E-Invoicing Solution
When choosing an e-invoicing solution, consider its potential to maximize operating efficiencies by automating financial processes. E-invoicing capabilities that are integrated into comprehensive business software suites can help companies achieve that goal. For example, leading ERP software can automatically generate e-invoices from sales transactions. Your solution should also be able to comply with requirements for document storage, calculating the correct taxes and including digital signatures where necessary. If your company does business internationally, look for a solution with capabilities such as multicurrency and multilingual support.
Simplify Invoicing With NetSuite
NetSuite automates manual accounts receivable processes, letting businesses quickly and easily produce e-invoices for greater accuracy, faster payment and better tracking. NetSuite accounts receivable automatically generates invoices from sales orders as they are fulfilled, eliminating the need for error-prone manual data entry. Finance teams can customize invoice templates to meet unique customer needs, offer a choice of payment options and send invoices via different methods, including email. When customers place multiple orders within one billing period, NetSuite automatically creates a single consolidated invoice — and when payment is received, the pertinent amount is allocated to each order.
NetSuite invoice management helps companies automatically process invoices they receive from their suppliers. When a purchase order, receipt and bill have been entered or received electronically, NetSuite executes a three-way match to correlate the documents for approval. The accounts payable team can then decide which bills to pay when, to optimize cash flow.
E-invoicing can transform what has traditionally been a labor-intensive process for many businesses. By automating invoice creation and processing, companies can boost operating efficiency, reduce errors and improve cash flow.
E-Invoicing FAQs
How do I create an electronic invoice?
Electronic invoices can be created manually, using a template, or automatically from a company’s business software. Some ERP systems can automatically create electronic invoices from sales transactions and send them to customers.
What is electronic billing and electronic invoicing?
Electronic invoicing (e-invoicing) involves creating and sending invoices electronically in a standard, structured format. E-invoices may be generated automatically by a supplier’s business software, and they may also be automatically processed by the customer. Electronic billing and electronic invoicing are similar terms. Both involve creating a digital bill that is sent to customers. Electronic billing usually also involves methods for electronic payment of the bill.
What is the difference between EDI and e-invoicing?
EDI is a technology that is used to exchange business documents, including electronic invoices. It was first developed in the 1960s. Businesses must connect to a specialized network to send or receive invoices. It’s mainly used by larger companies in a variety of industries. In contrast, most modern e-invoicing systems are internet-based and readily available to companies of all sizes.
Who is eligible for e-invoicing?
Any company can send e-invoices to its customers, as long as those customers can receive their bills via the internet or an online portal. In some countries, suppliers must obtain their customers’ consent.
What is the difference between an invoice and an e-invoice?
An e-invoice is a type of invoice that is in digital form and contains billing information in a structured format. This makes automatic invoice processing easier. It is sent to customers electronically via e-mail or through a secure portal.
What is electronic invoicing system?
An e-invoicing system enables companies to create and send electronic invoices. E-invoices can then be emailed to customers, or customers can access them via a customer portal. Electronic invoicing may be a feature of accounting systems or broader ERP systems.









