Embedded analytics drives actionable data analysis from within a business application. This article explores the benefits and capabilities of embedded analytics. These analytics may come from either operational or reporting systems.
What Is Embedded Analytics?
Embedded analytics provides fast, timely and helpful information by gathering, sorting, reporting and visualizing data from various sources and displaying that analysis within a business application. It automates the capturing and exporting of data, sorting it and creating reports and visualizations from a variety of data sources.
Key Takeaways
- Embedded analytics adds value by leading to cost savings for the business.
- Businesses in many industries now use embedded analytics solutions and adoption rates continue to grow.
- The decision to build or buy embedded analytics applications is a dilemma for organizations with technical product development and engineering resources.
- Companies should use a framework to assess their current analytics capabilities and review use cases to determine if a more advanced embedded analytics solution is right for their business.
Embedded Analytics vs. Business Intelligence
Unlike standard business intelligence (BI) applications, embedded analytics functions inside the user’s existing software application. The analysis doesn’t need separate dashboards, interfaces or additional accounts to deliver meaningful insights.
In-app embedded analytics provides faster, more intuitive data analysis and increases adoption and usage of analytics content. By delivering insights contextually, embedded analytics are well-suited for non-technical users or anyone looking to make data-driven decisions. Executives, IT personnel, data professionals, software engineers and product managers can query and extract actionable insights without leaving their existing environment to access separate reporting tools.
Benefits of Embedded Analytics
There are many advantages to embedded analytics in business processes. With the global market for embedded analytics forecast to top $60 billion in 2023 and come close to $116 billion in 2028 — a CAGR of 13.9% — according to one recent report, it’s clear that organizations around the world are grasping the benefits, as well. End users, focus groups and vendors report the following benefits of embedding analytics within their business applications:
-
A single source of truth for data analysis
-
Enhanced productivity and scalability
-
Improved customer satisfaction
-
Wider adoption across business functions
-
Simplified workflows and more easily deployed analytical capabilities
-
Self-serve, personalized analytics interfaces
-
Higher annual revenue from new revenue streams
-
Personalized data capture by user and role
-
Greater competitive advantage through product differentiation
-
Helps grow customer numbers, value and retention
The beauty of embedded analytics lies in its ability to mine volumes of business-critical data from the applications in use. This brings organizations significantly closer to realizing the above benefits, as well as being able to make quicker, more informed decisions.
Challenges of Embedded Analytics
The disadvantages of embedded analytics usually don’t outweigh the advantages. But to realize the benefits, you need to consider some critical questions and potential roadblocks.
-
Buy or build:
Building embedded analytics modules with in-house development expertise is a popular choice. However, the drain on core product development and the focus necessary to deliver this functionality can quickly offset the advantages of complete control, customization and design. If you need to deploy embedded analytics quickly, either internally or for customers, using a third-party out-of-the-box system might make more sense. Your developers may be able to leverage existing open-source libraries to build in-app analytics without end to end development.
-
Customization:
Customizing analytics experiences is one of the top challenges for users who need flexible tools that adapt to different data sources, infrastructure and legacy systems. Vet third-party vendors and inquire about API integrations, security features, deployment, developer support and source code libraries before committing to a solution.
-
Usability:
Embedded analytics packages should provide a superior user experience. The goal is to quickly put information in the proper context and empower data-driven, accurate decisions without requiring extra steps. Choose (or build) a solution that doesn’t slow down existing systems or create additional workflows that require switching applications, managing another user account and exporting data.
-
Scalability:
Paying a per user license for advanced embedded analytics capabilities can add up fast. Choose a provider that offers scalable, cost-effective tiers of service. They should have a proven track record of continuous, secure feature updates and upgrades that evolve with your needs and industry trends.
Who Uses Embedded Analytics
Many industries use embedded data analytics. The practice enjoys wide adoption rates and different use cases. The value of embedded analytics varies by how industries and companies monetize data. Some examples of industry specific use cases for embedded analytics are detailed below:
-
IT:
DevOps and DevSecOps teams leverage machine learning and AI with embedded augmented analytics to predict, monitor and report where security vulnerabilities will most likely occur.
-
Finance:
Investment bankers and brokerages use advanced embedded analytics dashboards to identify investment patterns, growth patterns and threats to uncover market volatility and identify opportunities.
-
Manufacturing:
Factories and warehouses that depend on supply chain partnerships leverage embedded analytics to report on key partner performance metrics without requiring adding workflows.
-
Healthcare:
Healthcare providers and medical personnel skilled in providing care, not analyzing BI data, can improve patient care by identifying actionable patient insights and adjusting treatment plans in real time.
-
Business Services:
Sales and marketing teams and management working daily within enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM) and HR platforms that offer embedded analytics don’t have to leave these applications to conduct analysis before making key decisions.
-
Retail:
Ecommerce retailers use insights to elevate the web and mobile experience for customers. They rely on engagement metrics driven by analytics embedded within the content management or financial system to monetize online trends by optimizing UIs, product mixes and checkout sequences.
-
Construction:
Contractors use embedded analytics to improve construction project outcomes and reduce risk. They use automated project reporting and integrated dashboards that combine data from disparate systems and solutions.
-
Government:
Public sector employees and agencies use embedded analytics reporting to share critical insights and progress reports with constituents and adhere to accountability and transparency standards and regulations.
-
Education:
Teachers and administrators use embedded analytics to discover trends in learning and assess students' testing performance using online learning platforms.
Embedded Analytics Implementations
Companies use embedded analytics to drive innovation and realize cost savings. Here’s how they use some of the tools to make the most of their insights:
-
Dashboards:
Decision-makers use embedded analytics on integrated reporting dashboards within existing business applications like ERM and CRM solutions. These make it easy for anyone to use in programs they already use to make real-time data-driven decisions.
-
Reporting:
Embedded analytics provide operational monitoring and reporting features to communicate across business units and locations. Users can share these reports with customers so they always know the status of their goods.
-
Service-level Agreements (SLAs):
Automatically sharing data with third-party software vendors can help monitor and improve service-level agreements (SLAs).
-
Customer Experience:
Software customers can use monetized data capture and analysis without add-ons or licensing requirements. They can use this data to scale up and grow their business.
-
Internal Development:
DevOps and engineers use the continuously growing datasets from multiple information sources to improve performance.
Common Embedded Analytics Capabilities
As with any technology purchase, a business interested in an embedded analytics tool must first assess its goals and the problems it wants to solve. From that should emerge a list of requirements and must-have capabilities. Consider the following capabilities:
- Data discovery, preparation and acceptance from a wide variety of data sources
- Fast data processing and response
- Self-service reporting
- Web-based integrations and third-party compatibility
- User-friendly native dashboards and other visualizations
- Intuitive graphical toolsets
- Automated static and interactive reports from streaming data
- Benchmarking and forecasting features
- Visual and predictive analytics in the form of dashboards are essential for real-time decision-making
- Mobile reporting capabilities
- Secure, user-restricted collaboration
Scalability is also an important consideration for growing business. Over time, the embedded analytics tool should be able to support increasing amounts of data and a larger employee base — all without any decreases in performance.
Future of Embedded Analytics
Embedded analytics will play a key role in solving problems and innovating how businesses capture, store, curate, visualize and share actionable insights. It will help shape how businesses manage the volume, velocity and variety of big data.
Machine Learning Algorithms and AI
Big data and the exponential growth of data capture will help to determine the future of embedded analytics. Many predict machine learning algorithms and AI programs will deliver more relevant, more important data to workers within their workflow. A very simple example of this is a sales projection based on previous quarters of sales and variance, that can do a forecast into subsequent quarters.
AI is making great strides in learning how to predict business trends, thereby reducing the workload for the people who need to analyze the data. Machine learning has the ability to analyze complex data sets. When combined with a BI system, machine learning can provide reliable recommendations for decision-makers.
Automated Data Discovery
The ability to automate data discovery and leverage embedded analytics within existing business applications will help to showcase the potential of data science across new business sectors. The simplicity and usability of modern embedded dashboards will empower more people to become knowledge workers. Organizations will be able to bring new levels of data science to various non-technical environments without adding specialized resources, replacing infrastructure or implementing new technology.
Example of Embedded Analytics Application
Kaiser Permanente is one of the nation’s largest not-for-profit healthcare organizations. Integrating embedded analytics with internal software applications helps Kaiser improve patient care analytics, make data-driven cost-control decisions and minimize risk at the point of care.
Kaiser Permanente uses an Electronic Health Records (EHR) solution integrated with a custom electronic disability documentation and communication tool called Activity Prescription Form (ARx). MDGuidelines, the flagship product of ReedGroup, is a proprietary set of embedded analytic content and capabilities for benchmarking and optimizing healthcare performance. The solution was integrated into ARx at Kaiser Permanente, becoming the healthcare industry’s first large-scale integration of disability duration tables delivered at the point of care.
Kaiser has a massive volume and variety of data. The structured data from different sources like billing and lab testing, combined with the unstructured data from patient visits (doctor notes and charting details), creates a unique challenge. Embedding ARx with robust analytics content, including evidence-based care guidelines, provides physicians with direct, easy-to-access analytics tools to survey critical patient data.
The results of a multi-year study on the ARx integration translated to an average savings of $66 million per year in wages, benefits and costs associated with lost productivity. Caseworkers and clinicians can estimate recovery time more accurately, reducing overall disability durations.
Is Your Company Ready for Embedded Analytics?
Deciding if an embedded analytics solution is right for you requires a clear understanding of your current BI maturity level and customer needs.
Use the following resources to determine if you should build embedded analytics in-house or buy a solution. These tools will help you evaluate where you fit on the curve of possible embedded analytics capabilities.
Embedded Analytics Maturity Curve Model

An out-of-the-box embedded analytics product may not meet all of your exact needs, but it should address most of them and have the flexibility to support specific use cases. Ask yourself how you’ll use it, how you’ll analyze the data and compare the difference between building an internal application to purchasing an integrated embedded analytics solution.
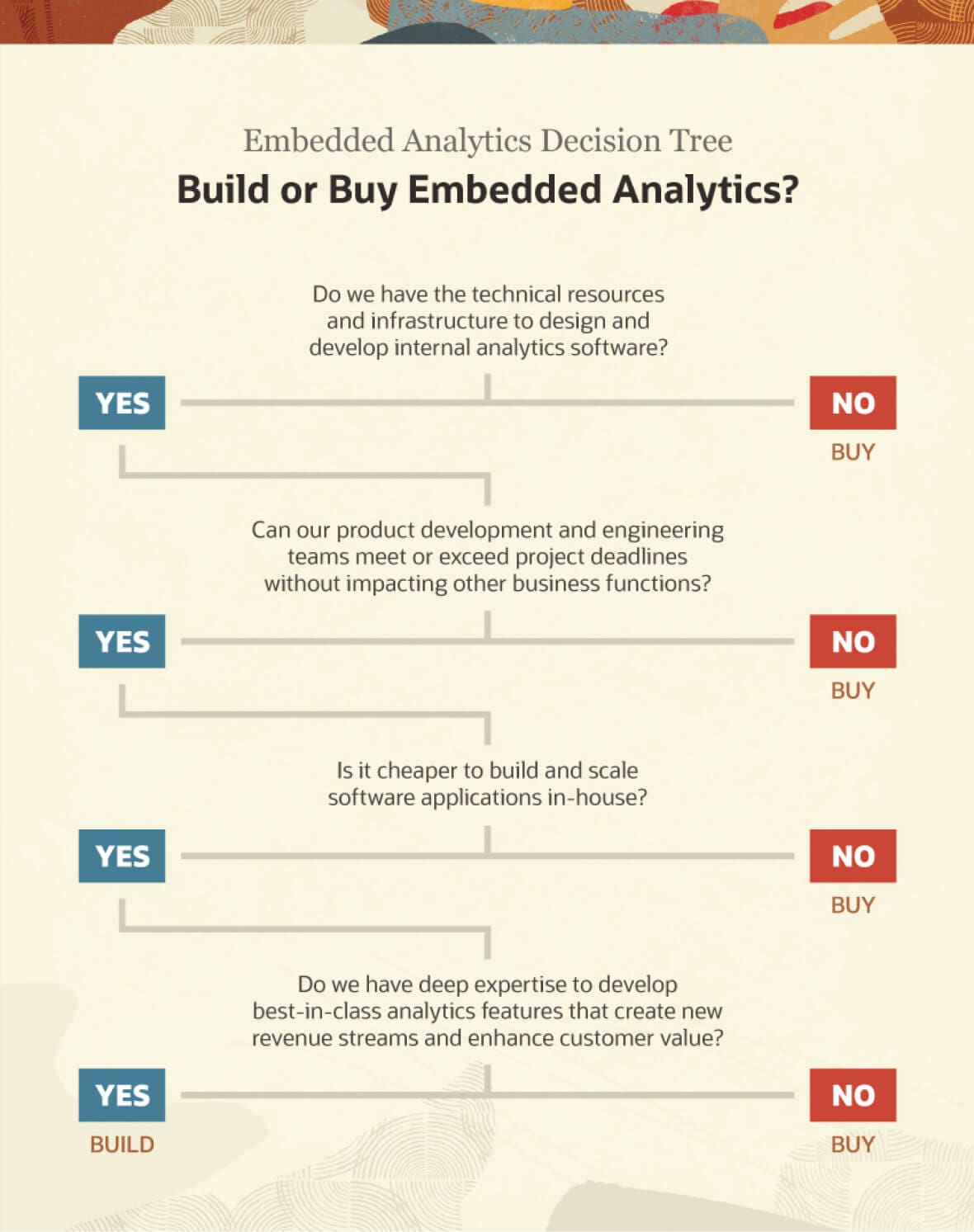
Embedded Analytics Decision Tree: Build or Buy?
The decision to buy or build embedded analytics software rests on a business’s needs, priorities, resources — time, money and expertise — and the nature of the business. Each question on the following decision tree should be explored among a diverse team of stakeholders before a choice is made.
Building the Business Case for Embedded Analytics
The amount of information relevant to business decision-making only continues to grow. Your business applications must deliver value from this data. Delivering actionable, real-time insights using intuitive dashboards and reports embedded within your existing applications is a critical advantage.
Embedded analytics provides faster access to actionable data that a company can use to identify new market opportunities, locate areas of the business for improvement, and offer intelligence that you can use to deliver an exemplary customer experience and reduce churn.
Why Do We Need to Embed Analytics in the Business Processes?
Embedding analytics can help you deliver more value to your employees and customers because employees spend less time hunting for data or seeking help in creating reports and more time delivering strategic value. Embedded analytics encourages everyone to embrace data analysis — not just the analysts and scientists.
NetSuite Embedded Analytics Solution Provides Actionable Business Analysis to Every Department
Close the gap between business intelligence and business outcomes by putting data to action without increasing existing workflows. Improve your understanding of your data’s business context and discover actionable insights with NetSuite’s unified platform, robust APIs and real-time business intelligence. NetSuite also provides embedded analytics enabling you to discover hidden information that can be used to make critical business decisions and gain insight across departments, teams and subsidiaries.
Embedded Analytics FAQs
What types of applications commonly use embedded analytics?
Embedded analytics can be integrated with many types of platforms and applications. They include enterprise resource planning, customer relationship management, financial management, inventory management, supply chain management, ecommerce and industry-specific tools.
How does embedded analytics enhance user experience?
At the broadest level, embedded analytics enhances the experience of users — meaning the employees who use it — by being part of the business applications they’re already using, without the need for separate dashboards, interfaces or anything outside of their direct workflow. That means quicker access to real-time data and actionable insights, to name two benefits.
Are there industries or sectors that benefit more from embedded analytics?
Every industry or sector that uses software stands to benefit from the use of embedded analytics. That includes organizations in IT, finance, manufacturing, healthcare, business services, retail, construction, government and education.








