When it comes to product information, there is one place in a company’s enterprise resource planning (ERP) system that supply chain analysts and operations employees alike can look to find a product’s suppliers, materials used to build it, unit inventory and even what margin the company is realizing on the product: the product’s item master data.
What Is an Item Master?
An item master is an organized collection of all pertinent information relevant to a specific product. Item masters are typically located within a company’s ERP system. (Note: The persons responsible for keeping the item master data record are also often called “item masters.”)
Item masters can be quite comprehensive; ideally, they should contain every piece of information that managers of many kinds, at any level in the organization, would need to inform decisions pertaining to the product. For large companies whose main economic activity is selling physical products, item masters are so important they’re sometimes called the DNA of the company.
Item Master vs Inventory Item:
An item master is a collection of records about a type of inventory item. Item masters tell business managers everything they need to know about inventory items of a certain type. “Item master data” refers to the information within one or more item masters, and “inventory item data” usually refers to information about a particular inventory item or type of inventory item. Not all collections of inventory item data will be item masters, but item masters are always populated with inventory item data.
What Is Item Master Data?
“Item master data” refers to all of the information contained in the item master for products in a company’s ERP system. Product managers, along with purchasing, sales and finance professionals, can use it to understand things like the value of the company’s inventory, manufacturing times and purchase price variances for materials — all of which are variables that can affect a product’s — and the company’s — bottom line.
The greater the detail contained in an item master, the better the company’s ability to optimize and improve the financial return they get on making, stocking and selling the product. At the very least, an item master should contain the item’s name, description and cost to manufacture, as well as its current inventory levels, its manufacturing lead time, its bill of materials, the sources and suppliers of those materials and the quantities of materials currently on order.
The item master in a company’s ERP should have those fields as a baseline. But to outfit the item master data with all the right information managers need to make decisions aligned with the company’s priorities, there will likely be more fields — for example, physical parameters are common — along with custom fields specific to that company or product, as determined by senior business leaders.
Item master data consists of useful inputs for analyses aimed at improving business processes, but it’s integral to day-to-day decisions and processes as well, particularly in supply chain management and inventory management. Good item master data, combined with sales data and forecasts, for example, will let a company be more accurate and forward-looking about when and how much to order from suppliers.
Item Master Data Explained
With accurate item master data, a company can make fast and effective decisions regarding the supply chain of a given product, like what types or colors of items move the fastest, what size sells most and which of the product’s variations are lagging in sales. Once business decision-makers know what colors or sizes of T-shirts sell the most, for example, they can adjust materials orders throughout the supply chain so that more of those colors and sizes can be produced.
So, by maintaining clean data, companies have a built-in source of operational intelligence that leads to better-informed decisions — which, in turn, improve revenue and profit.
Why Is Item Master Data Important?
An accurate item master record will ensure that productivity and workflow continue uninterrupted and without excess cost or unnecessary work. Keeping records about products accurate, up to date and in a central place can reduce misunderstandings and minimize costly errors as well. Maintained correctly, item masters will serve as the central hub for data that supply chain processes depend on for execution and adaptation.
If the item master is not accurate, a company may end up purchasing supplies late; purchasing those supplies in suboptimal quantities; leaving shipping logistics misaligned with customers’ needs; or making dozens of other mistakes that can have rippling effects on production, sales, customer relationships and — ultimately — profits.
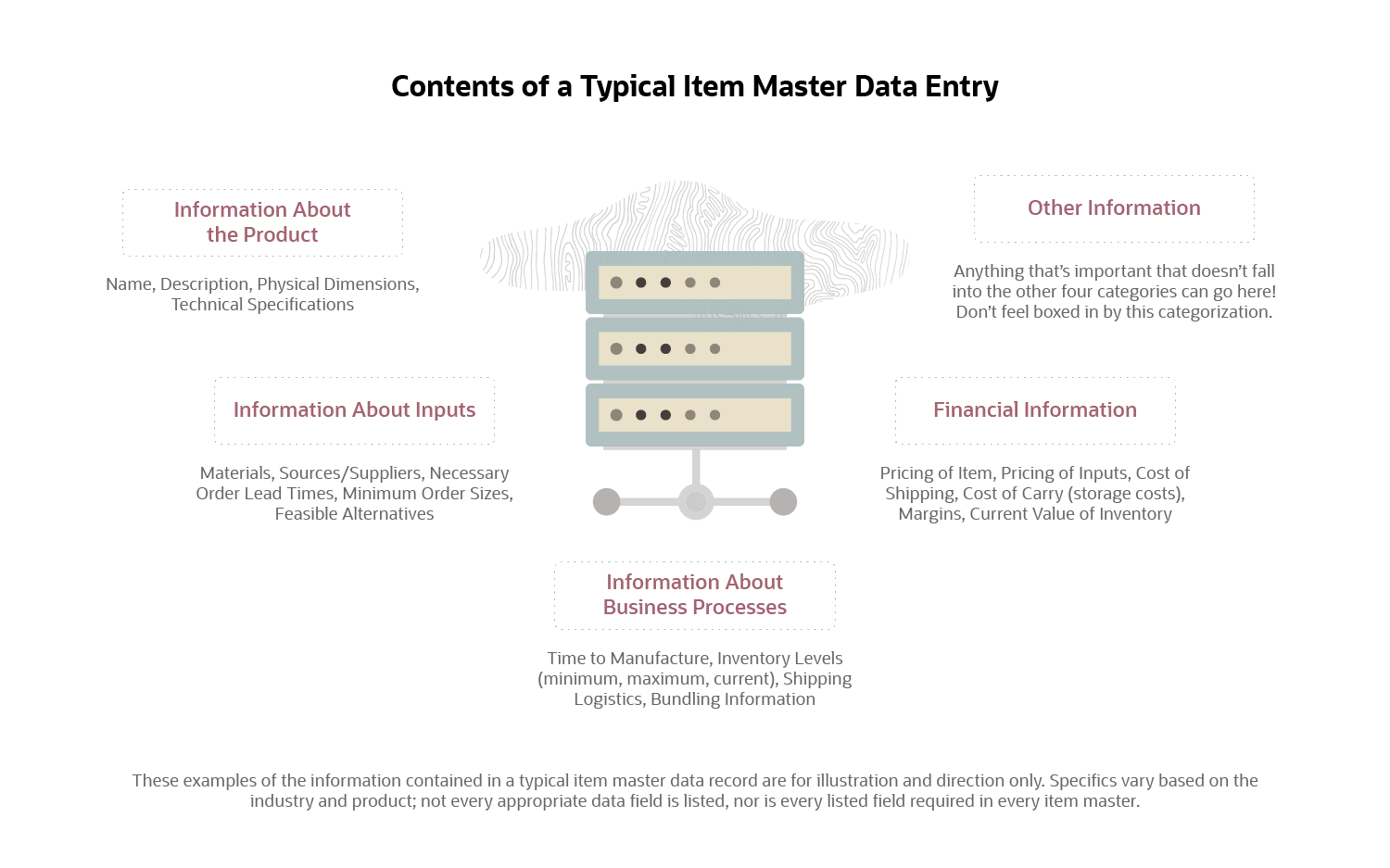
What Does Item Master Data Include?
Different businesses will need to track different information, but, in general, item master data will cover information about the product, its inputs, the business processes surrounding the product and financial information pertinent to the product. As listed above, a good baseline for fields to cover in an item master record includes item name, description, costs of inputs, BOM (bill of materials), materials sources, manufacturing lead times, suppliers, order quantities and inventory levels. Depending on the company and product priorities, an item master can also contain more detailed fields, like purchase cost, minimum stock levels and maximum stock levels.
It’s important to fit the structure of the data to the facts of the business. For example, a company with a dozen warehouses and hundreds of stores will need much more complex inventory tracking than a company with a single warehouse that sells everything online. Knowing how many units the whole company has in stock is great for the company with one warehouse, but that will often be insufficient information for the company with a dozen warehouses.
The item master is a dynamically evolving record and must be maintained to reflect up-to-the-minute data to correctly inform purchasing and other alerts sent by the ERP system to product managers and suppliers.
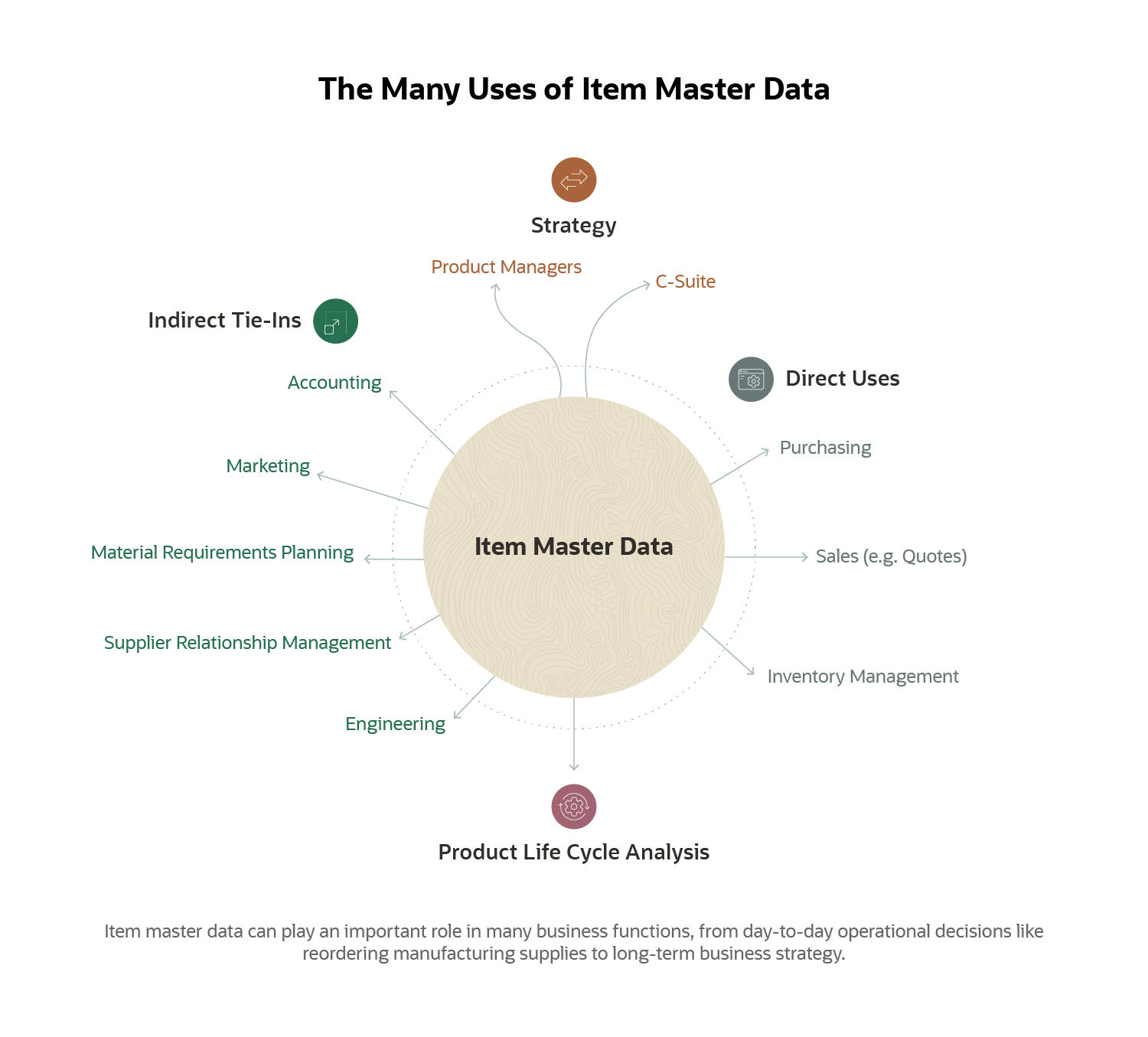
How Is Item Master Data Used?
Since item master data is a record of all costs, material requirements, suppliers, inventory and other important attributes about a product, the item master is the go-to source anytime someone in the company needs access to updated and accurate product information.
Role of the item master:
Item master data has several regular roles to play at multiple levels of company strategy and tactics. Overall, it helps companies realize value by providing clean and accurate data that feeds back to accounting, sales and engineering departments, each of which can manage their plans based on numbers provided in the item master. As such, item master data’s primary role comes into play for making day-to-day operational decisions about reordering from suppliers and maintaining stock levels when and where they’re needed. It also provides key inputs into valuing inventory, making decisions about staffing, diagnosing unexpected events or patterns in manufacturing and sales, and performing financial analyses for tracking and decision-making.
When a company is conducting product life cycle analysis, item masters become even more valuable than they are for day-to-day operations. Product life cycle analysis can identify key changes in purchase costs, inventory value and profit margin for the product in question. This analysis will, in turn, inform decisions regarding the health and profitability of the product.
Perhaps most importantly — albeit most rarely — item master data will be one of multiple sources of information used for making high-level strategic decisions about a product, product category or the company as a whole. It’s hard to chart a course to where a CEO wants the company to go without good information on where the company is, and item masters can provide an excellent metaphorical “you are here” marker along those journeys.
Quality of Item Master Data
The quality of data contained in a company’s item master is critically important to its business. Low-quality data can be even worse than no data at all: While both bad data and missing data can lead to bad decisions, low-quality data still costs money to collect and maintain and can give decision-makers a false sense of confidence.
For example, inaccurate inventory numbers for a consumer product in the months before the holiday season could result in an inventory shortage, and slower-than-expected delivery of materials could cause delayed production, delayed order fulfillments, order cancellations and an unhappy customer base. In cases where these problems were caused by low-quality data that management thought was great, the error could have further resulted in broken promises to customers and serious damage to the company brand.
Item Master Management Best Practices
Like all critical business functions, the effective formation and maintenance of item master data relies on adherence to industry best practices, including but not limited to the list below. It’s especially vital to establish and follow good procedures for item masters, because they have so many components that even a small increase in their error rate could create thousands of issues that employees would have to track down manually — if they’re noticed at all.
- Build a process. Understand what fields are most important to an item
master for your organization in terms of purchasing, inventory and analysis, and make
sure those elements are included in every item master as a standard. Develop a process
document to remove the guesswork from item master creation and to ensure efficiency for
your production line.
- Work backward from important decisions. When creating item masters,
it’s common to wonder what information is worth collecting and what information
isn’t particularly useful. Thinking about the kinds of decisions that need to be
made based on the data can help reveal what additional information would be most helpful
to have when the time comes. Tomorrow’s decisions will be informed by data you
decide to collect today.
- Create a standard template to reduce work. Data accuracy does not mean you have to re-create the wheel for each item master record. Build an item master template in the company’s ERP that employees can use to enter data for new products efficiently.
- Assign an item master librarian. Or two. These employees will be responsible for reviewing each item master record to ensure data quality and adherence to the process document. Consider this an extra check to help prevent costly purchasing and inventory errors.
- Plan for data interconnectivity. Item master data, when collected properly, can provide a powerful and robust source of information. But the data can be even more valuable when combined with other information, like sales forecasts or accounting information. Thinking about how to combine data sources can help you set them up to make that interaction much easier in the future.
Manage Item Master Data With Inventory Management Software
In maintaining effective item master data, a good ERP system is indispensable. Creating item masters and deploying their data usefully, even in a small product-based business, can be a major data aggregation task that requires scalable software integrated with business functions. To get the most value out of the data — such as simplifying inventory management processes, automating key analyses, improving employee efficiency and optimizing purchasing and production — companies need software that is both specialized and customizable. The data sets are large, and timeliness is too important to rely on spreadsheets and ad hoc analysis. A system like NetSuite Inventory Management that can scale with growing businesses provides these advantages on an ongoing basis.
A company’s item masters, like its financials, are a critical data repository that must be maintained and accurate at all times for the sake of the business. Well-maintained item master data helps businesses stay on top of inventory management, avoid overstocking and shortages, and inform high-level decisions about product lines (among many other benefits). Item masters require a lot of data — carefully collected and analyzed — but creating them doesn’t have to be difficult. With the right ERP software and solid processes in place, your item master data can perform as another building block toward the success of your organization.
Award Winning
Cloud Inventory
Item Master Data FAQs
What is Item Master in ERP?
An item master is an aggregated collection of records and data about a product or product type, including information about the product itself, its inputs, its unit economics (like cost and gross margin) and any other information a company deems an important input into product-tracking and decision-making.
Which fields can you create in item master data?
A company can add any data field it wishes to an item master. Some fields that are indispensable to one company (such as product color for a pillowcase maker) may be completely useless to another (such as product color for a computer chip manufacturer).
What does master inventory mean?
Master inventory can refer to the aggregated and authoritative tracking of a company’s or a store’s inventory. This can be synonymous with, or a subset of, the information found in a company’s item master data.
What is an item master?
An item master is a stored and amalgamated collection of the most crucial information and records associated with a product or product type.









