There's no two ways about it: The journal entry process is a tedious part of the financial close. It's a primary reason accountants burn the midnight oil at the end of each accounting period and why financial statements can be delayed beyond usefulness. But automating the process can change that dynamic. Journal entry automation is about linking systems, importing data, setting rules, programming recurrent calculations and more so that financial statements are more accurate, more timely, more easily audited and less at risk from possible fraud than when performed manually. Journal entry automation also allows staff to turn their attention to higher-value tasks. If this all sounds too good to be true, read on to become a believer.
What Is a Journal Entry?
Companies record every business transaction as a journal entry in their accounting books. In accordance with the double-entry method of accounting, journal entries contain debits and credits that increase and decrease a company's financial accounts. The journal entries are accumulated in a company's general ledger (aka "general journal"), either directly or indirectly through subledgers, such as sales journals and accounts payable journals. Account balances make their way into the lines on a company's financial statements, so it's critical that the originating journal entries are accurate.
Automated vs. manual journal entries:
Back in the day, journal entries were written on green, columnar accounting paper in leather-bound ledgers. The process evolved to include spreadsheets and manual entry into accounting software. Many businesses, large and small, still operate this way. However, more than 60% of a business's record-to-report process, which includes journal entries, could be automated, according to a 2021 EY report. Doing so can increase efficiency, reduce costs and result in more accurate financial reports completed more quickly.
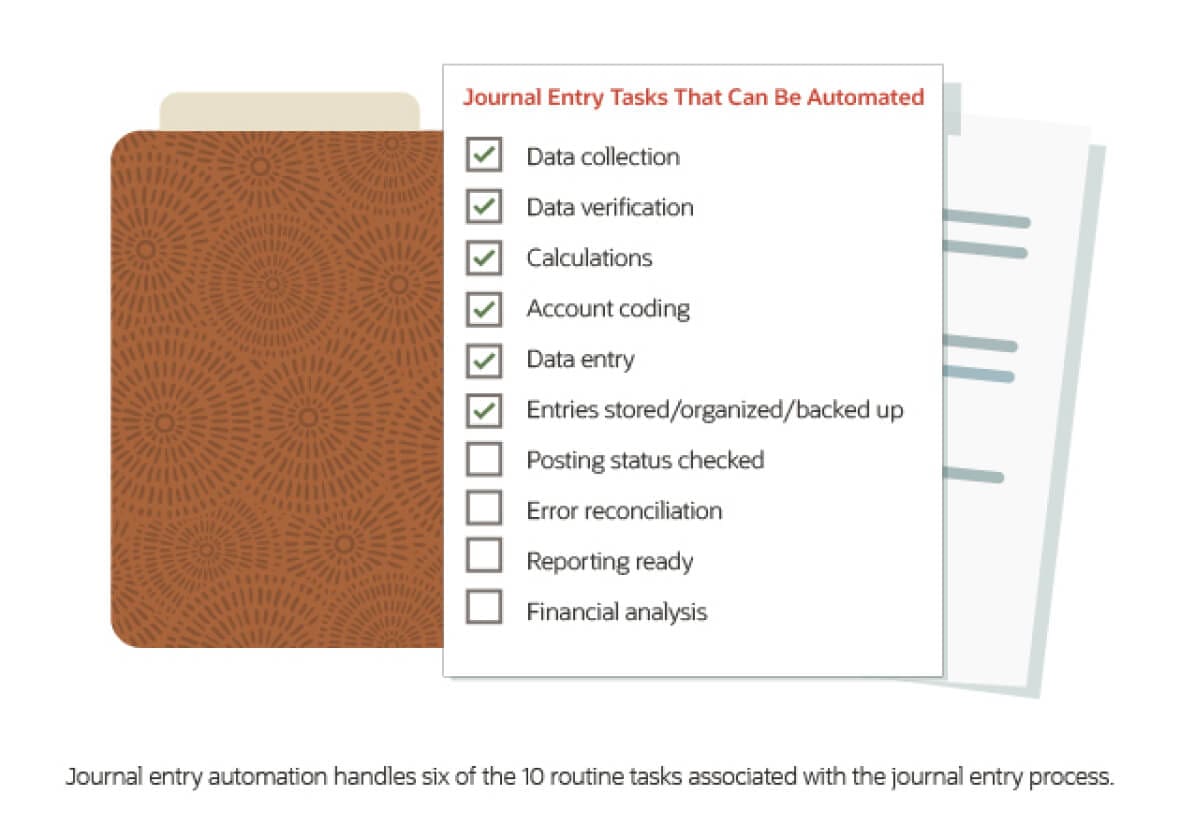
Key Takeaways
- Journal entry automation involves importing data from internal and external sources to originate journal entries in a company's general ledger.
- Journal entry automation relies on templates, preset rules and artificial intelligence.
- Benefits include enhanced accuracy, faster accounting closes, reduced labor and improved workflow.
- Technology with the most robust integration features can help achieve the greatest payoffs.
Automated Journal Entries Explained
Journal entry automation software ranges in sophistication. Simpler systems assist with journal entry creation, providing an interface to input journal entries. They also provide controls validating that account codes are active within a company's chart of accounts and that the journal entry balances debits with credits. Some software can upload full spreadsheets of journal entries, obviating the need to input each entry separately. Even simple systems like these are an improvement over manual, paper, binders and spreadsheet methods used in the past.
Journal entry automation can also streamline the posting — and subsequent tracking — of journal entries into the general ledger or subledgers, flagging potential errors for inspection, such as intercompany entries that don't offset each other. Related, journal entries can be set to automatically reverse in the subsequent period, such as for an expense accrual, helping accountants get a head start on the next period's financial close process.
Increasing in sophistication, journal entry automation may also handle the approval process with digital routing and review features. Automated journal entry dashboards can help accounting managers monitor progress and issues during the financial close process.
More advanced journal entry technology can automatically create journal entries using data that flows in from other systems. For example, depreciation expense journal entries can auto-post using data from an integrated fixed asset management system. Journal entry automation software can also accept external data to initiate journal entries, such as charges and fees on a company's bank statement. Additionally, calculation-based entries, such as provisions and deferrals, can be generated automatically. Finally, by using artificial intelligence, the appropriate information on digital or paper source documents can be used to generate an automatically approved journal entry if it falls within preset tolerances.
Journal entry automation does not eliminate the need for accounting staff; rather, it handles the tedious tasks so that accountants can spend more time reviewing and analyzing the numbers instead.
Journal Entry Challenges (or Dangers)
A single journal entry contains numerous components, including a reference number, accounting period/date, at least two accounts with their unique account codes, debits and credits based on calculations and supporting documents, as well as a description of the transaction. Now bear in mind that accountants even at small businesses may record hundreds or thousands of journal entries each month — and typically under pressure to close the company's books as quickly as possible. Within this context lies a host of accounting challenges when the journal entry process is handled manually, including:
-
Longer monthly closes.
Manual journal entry input is time-consuming. Errors hold up the financial close process even further because they require time to be remediated or investigated.
-
Inaccurate financial statements.
Undetected errors can cause incorrect information to flow through to financial statements and analyses, undermining their utility.
-
Labor inefficiency.
Valuable labor across the company can be mired down in either the tedious work of recording journal entries or providing the supporting information for them.
-
Increased potential for fraud.
The inability to keep up with the volume or complexity of journal entries can lead to insufficiencies in the review and approval process, which, in turn, increases the possibility of fraudulent activity slipping through the cracks.
How Does Journal Entry Automation Work?
Journal entry automation can expedite and increase the accuracy of the financial close process. At the same time, it allows accounting staff to spend more time reviewing and analyzing data, potentially uncovering profit-enhancing opportunities and reducing the risk of fraud. Many use-case scenarios involve importing external data into automatic journal entries, setting up rules that automatically calculate journal entries, as well as linking to other internal systems to prepopulate and auto-post journal entries. A few examples of how this works could include:
- A construction company links its fixed asset management system, which lists assets and related depreciation schedules for its heavy machinery, so that monthly depreciation journal entries can be automatically generated.
- A retailer imports sales data from its credit card processors, and the journal entry automation software automatically updates sales journals and creates new entries for processing fees, refunds and disputed charges.
- A professional services company receives digital bills from its landlord and utility companies, generating automatic journal entries that are preapproved within a +/- 15% relevant range.
- A restaurant with multiple locations but a single purchasing department avoids unmatched intercompany balances by using robotic matching on a continuous basis, rather than doing periodic manual reconciliations.
- A manufacturing company automates its overhead cost allocations across product lines by establishing an allocation scheme that automatically creates journal entries.
Benefits of Automating Journal Entries
Automating journal entries can lead to an accounting environment that is more accurate, more efficient and better able to focus on higher value tasks. At the same time, automation lowers several risks endemic to the accounting close process. Benefits of automating journal entries include:
-
Increased accuracy.
Reducing the degree of manual intervention in the journal entry process can cut down on errors in amounts, account coding and instances of journal entry duplication and omission.
-
Increased consistency.
Rules within the journal entry software ensure that transactions are coded consistently. Adherence to the company's accounting policies across business units is also bolstered.
-
Refocused staff time.
When the majority of journal entries are automated, staff can be redeployed to dealing with exceptions and to higher-level activities, such as reviewing, approving, reconciling and analyzing financials, rather than simply recording.
-
Streamlined workflow.
Digital routing for journal entry approvals becomes more efficient by reducing the incidence of process bottlenecks, reducing wasted time and frustration.
-
Faster accounting closes.
The combination of automated journal entries with redeployed manpower can help companies close their books more quickly. A continuous close is more easily achieved as well. Additionally, the increased transparency, streamlined approvals and process monitoring help resolve speedbumps more quickly.
-
Earlier access to information.
Information used for decision-making, such as financial reporting, forecasting and key performance indicator (KPI) analysis, can be available sooner because the financial close is completed more quickly.
-
Efficient backup.
Journal entry automation helps companies better organize and digitally store the supporting information for journal entries, eliminating the hassles and costs of paper storage.
-
Risk reduction.
Several features of journal entry automation — including less manual intervention, increased controls and earlier visibility into the data — can have the synergistic effect of detecting fraud faster and reducing the likelihood of it occurring.
-
Smoother audits.
Digital storage of journal entry supporting documents makes it easier for auditors to access data and verify transactions. Audits that run more smoothly reduce effort for all parties and can reduce fees.
Work Smarter and Automate Your Entries
Journal entry automation helps companies close their books faster, more accurately and with less manpower. It's a valuable tool that can help a company achieve the "work smarter, not harder" mantra. However, it's critical to choose software with robust features that go beyond just balancing debits and credits in an online interface. NetSuite General Ledger combines real-time bank integration, rules-based transaction matching with auto-posting of journal entries, such as amortization and depreciation schedules, profit and loss allocations and other routine calculations. As a result, journal entries are continually posted to the general ledger, alleviating the end-of-month crunch and enabling real-time visibility.
Conclusion
Journal entry automation can dramatically reduce the amount of manual intervention required, which increases accuracy, efficiency, consistency and ease of audits. At the same time, journal entry automation reduces the risk of fraud, document storage costs and the time it takes to close the books and access critical information for decision-making. The right journal entry automation software can help a company work smarter, not harder.
Journal Entry Automation FAQs
Can you automate journal entries?
Yes, journal entry automation software can turn imported, external data into automatic journal entries, use preset rules to calculate and automate journal entries, and integrate with other internal systems to prepopulate and post journal entries. Journal entry automation can make the financial close process quicker and more accurate.
What is automatic journal entry?
Journal entry automation comes in several forms and can dramatically reduce the amount of manual intervention typically needed. It increases accuracy, efficiency, consistency and ease of audits, while also reducing the risk of fraud and the time it takes to close the books and get critical information into the hands of decision-makers.
What are the steps to create a journal entry automatically?
Automatic journal entries are templated to include the major features of a journal entry, such as a reference number, accounting period/date, at least two accounts with their unique account codes, debits and credits based on calculations and supporting documents, as well as a description of the transaction. The automatic features include setting frequency, timing, automatic approvals, thresholds, etc.
How do you reduce manual journal entries?
It's estimated that about half of all journal entries can be automated with the right software, removing them from manual processing. Recurring entries, intercompany entries and those involving routine calculations and allocations are types of journal entries commonly converted from manual to automated.









