Every business considers its work to be important, but healthcare providers have the potential to truly change lives. Managing a healthcare business is particularly complex, with numerous departments needing to work in tight collaboration, with massive volumes of data to manage—all under strict regulations. The challenge for healthcare organizations is to seamlessly blend these moving parts, much like the well-coordinated efforts of an emergency room team during a medical crisis.
Enter enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, which connect everything from patient records and billing to inventory management and human resources. The best ERP systems simultaneously simplify processes, build operational efficiency, improve data accuracy, and help healthcare organizations maintain regulatory compliance. Properly implemented, ERP systems do the critical work behind the scenes to allow for higher-quality care.
What Is ERP?
An ERP system seamlessly integrates key business systems, such as finance, HR, customer relationship management (CRM), and manufacturing, into a single platform. This centralized command center allows companies to connect siloed operations to build greater efficiency and repository of companywide data to fuel smarter decisions about how to respond to market conditions and drive growth. ERP systems can be hosted on premises, in the cloud, or a combination of both, known as hybrid ERP systems.
Key Takeaways
- Healthcare companies often have complex operations that require intricate collaboration among departments.
- They also leverage massive amounts of data subject to intense regulatory scrutiny.
- ERP systems offer healthcare companies a way to securely manage their data while also helping them simplify processes, make smarter decisions, and ultimately improve patient care.
- Implementing an ERP system at a healthcare organization begins with thorough research and planning.
How Is ERP Used in the Healthcare Industry?
By integrating various functions, including patient records, billing, inventory management, and HR, into a single, cohesive platform, ERP systems can help healthcare providers improve data accuracy, simplify workflows, reduce operational costs, and improve patient care.
For example, ERP systems can track patient billing and insurance claims more efficiently, reducing errors and delays. They can also manage staff scheduling and payroll, so healthcare providers can focus more on patient care, less on administrative tasks. ERP systems automate inventory management so that the right amount of medical supplies are always in stock, reducing waste and helping ensure the best patient care.
Beyond these benefits, ERP systems have also helped healthcare companies handle one of their biggest challenges: maintaining accurate and up-to-date patient records that comply with strict privacy regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). The amount of data healthcare companies manage is staggering. The most recent statistic, from 2020, indicates that the global healthcare data volume was 2.3 zettabytes (or 2,300 exabytes). As a reference, recording every word ever spoken would represent just 5 exabytes of data. An ERP system’s secure and centralized database makes storing, processing, and maintaining large amounts of data much more manageable by giving healthcare organizations a single source of clean data across multiple integrated systems. Patient information is easily accessible to only authorized personnel, safeguarding against data breaches. This centralization has the added benefit of driving better coordination among different departments, improving overall patient care and operational efficiency.
What are the 9 Steps to Implement ERP in Healthcare?
Every ERP implementation presents its own unique challenges based on a healthcare organization’s specific circumstances. In general, however, following these nine steps can help ensure the best possible outcome.
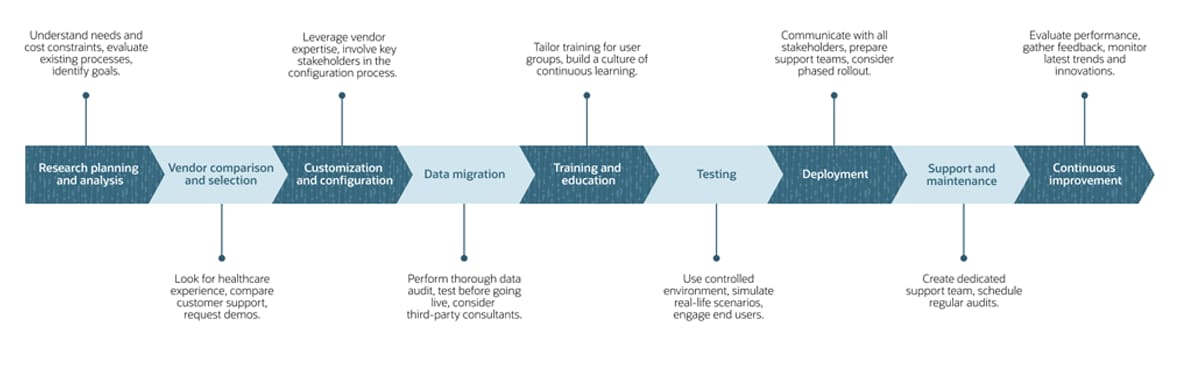
1. Research, planning, and analysis: The first step in the ERP implementation process involves understanding specific needs and cost constraints, evaluating existing processes, and identifying the goals the organization aims to achieve. Given the healthcare industry’s complex regulatory environment, careful attention should be paid to data security and privacy. Be sure to involve stakeholders from across the organization early in the planning process to gather insights, establish alignment across business units, and develop a clear, achievable roadmap for implementation. Experienced consultants can also provide valuable guidance tailored to any unique demands.
2. Vendor comparison and selection: Choosing the right ERP vendor is arguably the most crucial step in the implementation process. It’s paramount to assess vendors with experience in the healthcare sector—those that understand the industry’s regulatory and data security challenges and other specific requirements. Next, compare each vendor’s ability to integrate with existing systems and the level of ongoing support provided. Thorough due diligence should include requesting demos and case studies and seeking feedback from other healthcare organizations that have implemented the vendor’s solutions. Security, scalability and customizability will likely weigh heavily in any final decision.
3. Customization and configuration: Few software solutions can address a company’s needs right out of the box, which is why healthcare organizations must consider how an ERP solution can be customized for their specific regulatory compliance, data security, and integration challenges. For example, an ERP system must accommodate the diverse needs of different departments, which can require integrations with electronic health records, laboratory information management systems, and medical imaging software. The ERP system also might need to connect with pharmacy management systems, patient management systems, and billing and insurance platforms. In many cases, leveraging the ERP vendor’s expertise to tailor the system to specific workflows can be extremely helpful. It’s also important to involve key stakeholders in the configuration process and conduct thorough testing before going live.
4. Data migration: With the exception of the choice of vendor, data migration is widely considered the most important step in a healthcare ERP implementation. For the system to work properly and deliver on expectations, all patient records, financial data, and operational information must be accurately transferred from existing systems to the new system without loss or corruption. Data integrity and regulatory compliance are particularly critical here. Success requires a thorough data audit, including deleting redundant or outdated information, and careful testing in a controlled environment before going live. Experienced data migration experts can be worth the investment in this stage to mitigate risks and deliver a smooth transition.
5. Training and education: All staff members, from administrators to clinicians, need to understand not only how to use the new ERP system effectively, but also why its success is so important. With so many skill levels and roles in a healthcare setting, it’s essential to tailor training programs for different user groups. Use a mix of hands-on training sessions, ongoing support, and comprehensive user manuals. Most important, use the launch as an opportunity to build a culture of continuous learning and feedback that helps staff adapt.
6. Testing and quality assurance (QA): Given the integrations required in a healthcare ERP system deployment and the importance of accurate, secure data for both regulatory compliance and positive patient outcomes, it’s vital to test the system to verify that it meets all requirements. Testing should be conducted in a controlled environment, simulating real-world scenarios and engaging end users in the testing process to identify potential issues early. Constant feedback and iterative improvements are essential to making sure the system is reliable, efficient, and compliant.
7. Deployment and go-live: Hitting the launch button for an ERP implementation is the culmination of a lot of hard work, but healthcare organizations should also have comprehensive planning and risk management strategies in place to minimize disruptions to daily operations. Many departments will be affected by the launch, so be sure to communicate with each of them to ensure that all staff members are prepared for the switch. A detailed go-live plan should include clear communication with all stakeholders, with support teams ready to handle any issues that arise. Consider a phased rollout, allowing for adjustments based on real-time feedback.
8. Post-implementation support and maintenance: While a successful ERP deployment is a time for celebration, it’s not the end of the process. It’s merely the beginning of a new phase that includes continuous training, regular system updates, and rapid issue resolution to keep the system running smoothly. Ever-changing healthcare regulations put a premium on timely updates to maintain compliance. It’s also important to constantly monitor system performance to assure it can scale with increasing volumes of transactions and data. In this phase, establish a dedicated support team, schedule regular system audits, and build a culture of constant learning, using feedback from all users to identify areas for improvement.
9. Continuous improvement: ERP implementations are ultimately a marathon, not a sprint. Over the long haul, healthcare organizations should shift their focus to regular performance evaluations, gathering user feedback, and staying updated on the latest industry trends and software innovations. It’s important to stay ahead of evolving regulations and integrate new technologies without disrupting operations. Ongoing training, as well as ongoing monitoring and refinement of ERP processes, also play an important role in success.
Drive Intelligent, Human-Centric Healthcare With NetSuite
NetSuite’s solutions are designed to support a human-centric approach to healthcare with tools that help improve both operational efficiency and patient outcomes. NetSuite ERP’s integrated suite of applications seamlessly integrates financial management, inventory control, and HR modules to drive data-driven decisions, improve workflow efficiency, and deliver higher-quality care.
This integration reduces data silos and fosters collaboration across departments. One important benefit of NetSuite ERP for healthcare organizations is its ability to automate routine tasks, freeing up clinicians and other professionals to focus more on patient care. NetSuite’s completely cloud-based architecture delivers scalability and flexibility, so healthcare organizations can adapt to changing needs and regulatory requirements without significant disruptions. Built-in features help healthcare providers prioritize data security and patient privacy to stay aligned with regulations.
Implementing ERP systema can be complex, but they can dramatically improve how healthcare organizations operate. Perhaps their most important value is their ability to free healthcare organizations to focus more on what truly matters: delivering high-quality care and improving patient outcomes.
#1 Cloud ERP
Software
ERP Implementation in Healthcare FAQs
What is the difference between healthcare CRM and ERP?
In healthcare, as in other industries, customer relationship management (CRM) systems are often a component of larger enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. CRM systems in healthcare focus on managing interactions and improving engagement with existing patients, as well as marketing to and acquiring new patients. ERP systems are more comprehensive systems that integrate and automate back-office functions such as finance, HR, and supply chain management.
Do hospitals use ERP systems?
Yes, hospitals use enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to integrate and streamline administrative and operational processes. Like in other industries, healthcare organizations use ERP systems to manage finance, HR, procurement, inventory, and supply chain functions, while helping ensure compliance with regulations.
What are five major steps for successful ERP implementation?
There are many steps to a successful enterprise resource planning (ERP) implementation. Five of the most important steps are thorough research and planning to understand organizational needs, careful vendor selection to find the right solution, detailed customization and configuration to tailor the system to specific workflows, comprehensive training and education to promote smooth adoption, and continuous post-implementation support and maintenance to address issues and optimize performance.
How can ERP be implemented?
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems can be implemented by first conducting a thorough needs assessment to align the system with organizational goals. Then, carefully select and customize the ERP solution to fit specific workflows and follow up with a comprehensive training program for all users. The next step is to migrate existing data into the new system and conduct rigorous testing to confirm it functions properly. After go live with the system, provide ongoing support and maintenance to optimize its use and address any issues.









