Sales is powered by information and data. The more you know about your customers, their needs, and their history with your company, the more effective your sales team can be. But between managing relationships with clients, following up on leads from marketing, and all the other tasks salespeople have to complete, oftentimes the more manual and organizational tasks go by the wayside—which is why businesses that maintain ongoing sales relationships should consider a customer relationship management (CRM) platform.
A CRM does more than just organize information—it brings all of your customer relationships and sales processes into one central database that holds everything from communications to contracts and payments. For many businesses, a CRM is a lynchpin that the company couldn’t function without.
But CRMs are complex systems that often carry a significant price tag. If you are considering a CRM for your business and need to prove the numbers to the CFO, you’ll want to know the return on investment (ROI) for a CRM.
What Is a CRM?
CRM systems are digital tools that companies use to collect and analyze customer data, communications, sales activities, and service records. These centralized systems automate inefficient manual processes, such as spreadsheets, paperwork, and disjointed email inboxes, to help businesses more effectively serve their customers, even when multiple employees or departments are involved. Sales, marketing, and customer service teams use CRM software throughout the customer life cycle, from initial contact to lifetime value analysis. This allows staff to better understand customers’ needs and improve the quality of their service for both immediate requests and long-term planning initiatives.
Why Does Your Business Need a CRM?
Many small to midsize businesses cobble together spreadsheets, emails, and other disjointed systems to manage customer relationships. But this is inefficient and can often lead to negative and unorganized customer experiences. A CRM platform wraps up everything from sales to product or service delivery into a single system that any member of your team could use to brush up on a specific customer relationship instantly.
Here are five ways CRM technology can benefit your business.
Manage Leads
When the lead-to-sale process is the primary source of new revenue and growth, it’s important to give every lead first-class treatment. A CRM can capture details about a prospective customer when they submit landing page forms or talk to a sales rep. When businesses keep notes about all their prospect interactions, such as marketing campaign engagement, website browsing activities, sales estimates, and support tickets, they are able to provide more engaging and relevant brand experiences.
Improve Customer Support
Almost everyone has a story about bad customer service. When your customer service team uses a CRM to track customer relationships, you may be able to avoid bad customer service stories about your company.
CRMs feature logs of emails, calls, notes, and assignable tasks. This helps everyone at your business share documentation of every customer interaction while managing tasks in a way that keeps issues from slipping through the cracks.
Increase Collaboration Across Departments
A focus on collaboration can boost your customer experience. It doesn’t matter if workers are on the same floor, time zone, or even the same continent with a cloud CRM. Everyone has access to a single, reliable, secure dataset that brings teams closer together even when they’re physically far apart.
Delivering even simple product orders may require input from multiple people in disparate departments. More complex products and services can require dozens of staff. Each team shouldn’t use its own system in a silo. A central CRM will help workers share information and prevent redundant efforts.
Increase Efficiency and Productivity
A CRM can improve efficiency and productivity in multiple ways, including a better experience for your internal users. While customers will enjoy not having to explain a need repeatedly, your team will save time only having to collect that information once.
To further boost productivity, many repeat processes can be automated with a CRM. Automated marketing communication, sales pipeline tracking, integrated billing, and customer self-service features can save your workers hours every month compared with manual tasks.
Boost Sales
Many of the immediate benefits of a CRM focus on cost savings that impact your bottom line. But over time, you should see your CRM also help your top line, or gross sales, as well. Your sales team should find the information to put together relevant, high-quality sales presentations finely tuned to meet each customer’s unique needs.
Sales are the lifeblood of most businesses. With a quality CRM in place, you should see an increase in sales productivity.
What Types of Industries Should Invest in a CRM?
Virtually any industry that has repeat customer contact or any type of sales may benefit from a CRM. Here are examples of industries where CRMs are particularly popular and useful.
- Retail: Retailers can use a CRM to track customer interaction across different platforms like social media, phone calls, and emails. For higher-end sellers, CRMs allow you to create and track unique client profiles to keep each customer engaged with your brand.
- Finance: Banking, investment, and other financial services companies use CRMs to track customer needs and preferences. Some platforms include extra security and customized functions for tracking and managing customer finances.
- Hospitality: Hotels, restaurants, airlines, and tourism companies use CRMs to track guest preferences and drive automated marketing campaigns.
- Insurance: Small agencies and large companies can use CRMs to track customer profiles, keep customers engaged, and regularly assess needs to offer relevant products and coverage options.
- Consulting: Consulting businesses rely heavily on CRMs to track ongoing sales efforts and customer service needs. By fully integrating a Professional Services Automation (PSA) tool with CRM, advising and consulting firms can incorporate client project details back to their customer profiles.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturers often rely on ERPs to track incoming materials and outgoing sales. CRM modules offer robust communication and customer tracking so every order can be delivered accurately and on-time, meeting or exceeding customer expectations.
- Wholesale: Wholesalers can use CRMs for customers, as well as vendors.
This is far from a full list. Technology, legal, education, mining, transportation, real estate, telecommunication, publishing, healthcare, utility, infrastructure, printing, and many more businesses use CRMs for daily needs.
Measuring CRM ROI
The same basic formula will help you measure the ROI of any investment. First you identify the gain from the investment, subtract the cost, and then divide that by the cost and multiply by 100. The tricky part is understanding the real gain from the investment—after all, you may have other simultaneous efforts to boost your business’s bottom line like hiring new salespeople, expanding into a new market, or rolling out a new product line. Looking at multiple metrics simultaneously can add nuance to your calculations. Consider factors such as improved sales, customer retention, and other sales productivity metrics to understand the benefits of your investment. We go over more details about metrics that can shed light into ROI for your CRM later in this article. But let’s start with the basic, overall formula. To measure the return on investment of your CRM, use this formula:
ROI = (Net return on investment / cost of investment) x 100
Here’s an example to help you put that formula into action. Let’s say a business spent $12,000 on a CRM in one year and saw its gross margin, or a company’s net sales revenue minus its cost of goods sold, increase by $75,000. The ROI would be:
= ($75,000 – $12,000 / $12,000) x 100
= 5.25 x 100
= 525%
Key Metrics for Tracking CRM Performance
The ROI formula simplifies a lot of numbers behind the scenes. To understand where you’ll see both cost savings and revenue improvements, focus on these key metrics.
Not only can a CRM help you boost your bottom line, it’s also an essential tool to help gather and track data to inform KPIs. In simple-to-understand dashboards, you can track sales, efficiency, and team metrics all from the software. You can share this information with key stakeholders to demonstrate the ROI of your CRM and show performance of your team and how you’re progressing toward team and personal sales goals and quotas.
Business Metrics
-
Cost Savings
- Team or department productivity: With a CRM in place, you should see a notable uptick in collaborative productivity. Each team should be able to get more done with fewer resources.
- Efficiency savings: Individual workers should also become more efficient, as they have quick access to customer and product data from one central system.
- Process improvement: While a CRM may improve existing processes, you could find that you completely retool procedures around your CRM for improvements across the board.
Keep track of these key metrics to get insight to productivity, savings, and process improvement with a CRM.
- Revenue: Track the amount of sales revenue before and after implementing the CRM for your department at large, as well as per employee. By attributing new customer acquisition and sales to specific marketing campaigns, businesses can fine tune their strategies to drive more revenue.
- Average sales cycle length: How long does it take for a customer to go from initial contact or opportunity stage to a sale? A CRM should help remove bottlenecks that could otherwise slow deals with improved communication and more efficient processes. Monitor the time it takes on average from the time a customer is first contacted to when a sale is made.
-
Average deal size: Monitor the average price of each closed sale and
average it across your
sales team. You can also look at average deal size for different regions or even
individual employees.
Average deal size = Total dollar amount of all sales in a specific time period / total number of sales in the same period
-
Other sales productivity metrics: Sales data can be difficult to track
because it often relies
on time-strapped reps to manually enter data. Much of that manual data entry can be
automated with your CRM so
you can identify and monitor leading performance indicators of items you know could
eventually lead to sales.
Consider items such as:
- Emails
- Calls
- Meetings with clients
- Quotes sent to clients/potential clients
- Break-even point: Break-even point is a common metric calculated alongside ROI. The breakeven point happens when ROI equals 100%.
- Profit gains: Additional net gains beyond 100% ROI boost your bottom line. Most businesses should see significant profit gains when properly implementing a CRM.
Sales Metrics
-
Margin rate: The margin rate is the percent of each sale kept for
profits. A CRM may help
improve your margins and automatically track them. Track this for individuals, as well
as your entire sales
department, or by other cross section, such as region or location, for even more insight
into your data.
Average profit margin = Net income / net sales
- Sales revenue increase: Benchmark your monthly sales before the CRM goes live. An increase in average monthly sales is a useful metric to measure success with your CRM.
-
Sales Cycle Efficiency
- Total number of sales calls against total sales: A higher rate of sales compared to calls indicates a more effective sales process.
- Time to close: Shorter time to close means your sales team can more quickly move on to the next sale.
- Close rate: CRMs are excellent for tracking close rates by salesperson, team, and overall. A new CRM can power your sales team and lead to higher close rates.
- Sales volume: Track the total number of completed transactions over specific products, regions, or sales teams across time periods. CRM systems’ built-in analytic tools can also assess which areas drive the highest volume and identify potential growth opportunities, informing future marketing and resource allocation decisions.
Key Marketing Metrics
- Number of leads generated: In addition to closing sales at a higher rate, your team may see an uptick in potential sales with a higher number of leads generated. Leads can come from a variety of sources, so it is important to track where they came from to ensure they are valuable and converting into sales; especially if you are paying to acquire them. Whether leads come from landing page forms on your site, email newsletter sign-ups, or social campaigns, all the customer data is centralized in one digital environment.
-
Cost per lead: Because your CRM can help you more efficiently manage
your customer data and
automate time-intensive tasks like data entry, expect your cost per lead to drop. This
metric can help tie your
marketing to your sales.
Cost per lead = Total marketing spend / total new leads
- Revenue generated by campaign: CRMs make it easy to automatically attribute leads and sales by campaign, leading to detailed campaign-level reporting. Companies can configure their attribution based on particular models like first-click, last-click, or view-through within a specific window of time like one week or one month.
Key Service Metrics
- Number of cases by agent: With added efficiency, customer service agents should handle a higher number of cases per day.
- Cases closed the same day: Customers should enjoy a faster resolution. An increase in cases closed the same day is a win-win for customers and your business.
- Average time to resolve: Better data and internal communication should lead to a lower average time to resolve customer service cases.
- Customer satisfaction level: Many businesses can’t survive without repeat customers. The CRM should improve overall customer satisfaction, trackable in the CRM with customer surveys and other metrics.
- Customer retention: What keeps a client coming back is a mix of factors but receiving best-in-class customer service usually helps. CRMs make managing customer relationships across sales, customer service, and other teams much simpler. Track customer retention before and after the implementation of a CRM to measure its impact on keeping clients.
What ROI Should Businesses Expect From a CRM?
CRM software comes in all shapes and sizes—as does its costs and expected returns. You may find some basic CRMs for free, but often those lack the security and functionalities that more useful tools offer—such as the one included as part of the overall NetSuite product. Fully featured CRMs are powerful tools that can drive sales and securely manage your data. The price for the CRM often scales with your business size, and you should also consider any setup and training costs. However, experienced business leaders know that when a CRM is used well, those costs will pay for themselves multiple times over.
Businesses leverage their CRMs to increase conversion rates, but actual ROI results vary by business, industry, organizational preparedness, and the stage of rollout. Companies with successful CRMs typically see high returns in annual revenue, customer retention, and lowered costs/improved efficiency. Even already successful sales teams can benefit from added productivity, automation, communication, and transparency provided by a CRM.
10 CRM Features That Drive ROI
While this is only scratching the surface of what a CRM can do, here are 10 features that drive ROI.
- Automated order fulfillment: The moment a customer order goes in, the CRM can trigger the fulfillment process, looping in external vendors and your internal team.
- Customer support: Data gathered from email, phone, chat, and in-person customer support are collected with a single system for all users to access.
- Cross-selling: Data and customer insights enable enhanced cross-selling. Your CRM may be better at noticing customer needs than your sales team.
- Upselling: In addition to cross-sales features, the CRM may suggest potential upsells at higher service levels.
- Automatic renewal: Don’t let customer renewal dates slip by. CRMs can automatically process payments or send out invoices when it’s time to renew or order again.
- Quote delivery: For complex sales, you can build and deliver a quote within the CRM. If the customer wants changes or wants to accept, both can be done in the system.
- Web-to-lead forms: If you’ve ever filled out a form with a company online only to get a call from a human moments later, the company may have been using a CRM that includes web-to-lead forms. Have your sales team standing by to capture and capitalize on hot leads almost instantly as they come in.
- Customer portal: A web-based customer portal allows your customers to log in, review their information, update payment methods, download contracts, request customer support, enter orders, and more.
- Sales forecasting: Sales forecasting features help you plan for staffing and plan costs appropriately without overspending.
- Commission pay management: Automated commission systems save your accounting team and managers time. Sales staff may log in and see live data on their quota and next commission payment. Less time spent on payroll means cost savings and more time spent focused on customers.
How to Improve Your CRM ROI
Maximizing the return on a CRM investment requires careful planning and ongoing attention to how the system is running and how employees are using its features. These six strategies can help increase the ROI and effectiveness of a CRM system.
- Audit your data sources: Regularly review the quality and completeness of the data powering the CRM, and clean up duplicate records to ensure that all customer information is accurate. Ongoing updates to data entry standards can also improve data quality and minimize missed opportunities and inefficiencies that can hurt the systems’ effectiveness and ROI.
- Leverage automation: Identify manual, repetitive, and error-prone tasks that CRM software can automate. From email follow-ups and receipt templates to order processing and reporting, automation can reduce labor costs, minimize mistakes, and give customers a consistent experience.
- Solicit user feedback: Create channels for ongoing input from sales, marketing, and service teams about how the CRM system is functioning and impacting workflows. By understanding pain points and improvement opportunities, IT departments and CRM support teams can implement targeted fixes that address the needs of the people who directly use the system.
- Provide comprehensive training and support: Invest in ongoing training programs to make sure all users understand the CRM’s capabilities and best practices, including data entry protocols. Well-trained staff are more likely to use the system effectively to increase their productivity and contribute to a positive ROI.
- Drill into customer segmentation: Generate detailed reports by using the CRM’s analytics tools to better understand the behavior, value, and needs of different customer segments. This granular analysis enables more targeted marketing campaigns and personalized services that can drive higher conversion rates and customer loyalty.
- Integrate with other systems: Connect the CRM with other business software, such as accounting, marketing, order fulfillment, and customer service systems. Seamless data flow among these systems gives staff a more complete picture of customer accounts and orders when assisting them. Furthermore, benefits flow both ways, as CRM data can also be used to strengthen other systems, such as using expected sales to inform cash flow forecasts and revenue projections.
Boost Your Business With the Right CRM
A CRM is a pivotal tool for businesses with sales teams, companies that manage marketing, and organizations that create quotes and invoices or want to prioritize customer service. A CRM is a set of tools to help you better manage your relationship with customers and potential customers so you can grow your business.
But not all CRMs are created equal. The most robust CRM platforms connect with other ERP software, such as your accounting platform. This can benefit both those involved in marketing and sales, as well as other areas of your business like finance and even payroll. For example, your accounting team might need to understand commissions when running payroll. And your sales team might want to see a specific customer’s order history, outstanding payments, and other information to create an accurate quote. Of particular note is the configure, price, quote process that pulls information from your ERP and CRM platforms. Integrating CRM and ERP software can improve efficiency, connect teams, and provide more information for all involved to better serve your customers and boost your bottom line.
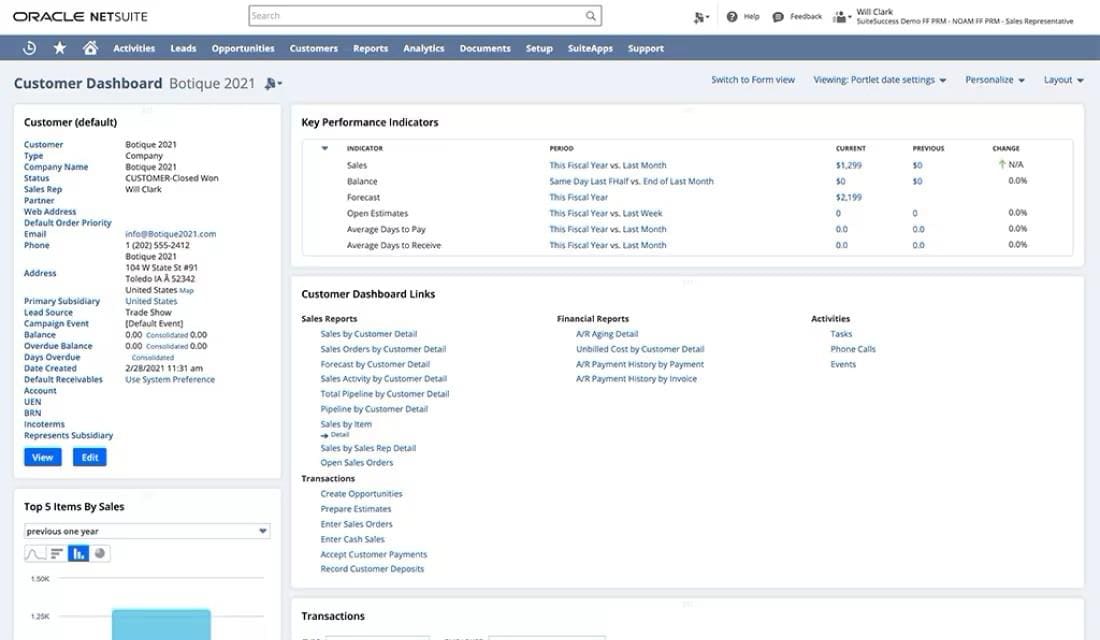
NetSuite’s Customer Dashboard
Video: Rural Utility Service Centralizes Communication in NetSuite CRM
Implementing a CRM is an investment in the future of your business. But like any major expenditure, it’s important to understand the financial impact and gain and assess the efficacy of the investment on a regular basis. To calculate the ROI of CRM software, you first have to understand savings, increased sales, and improved customer satisfaction as a result of the new tool. This is done by monitoring not just one, but many CRM KPIs, such as average deal size, margin rate, and customer retention. Fortunately, many CRM platforms can help serve up the KPIs in easy-to-understand dashboards so you can better report on the financial performance of your investment. And advanced CRM software connects to other important areas of your business, such as accounting, through ERP platforms so all your customer and sales data lives in one digital environment.
CRM ROI Frequently Asked Questions
How do you calculate CRM ROI?
CRM stands for customer relationship management. Return on investment (ROI) is based on the returns from the CRM over the cost, considering factors such as improved sales, customer retention, and other sales productivity.
What is ROI rate?
ROI rate is the return-on-investment rate. ROI tells you if your investment earned a profit and how well it performed compared with the initial investment amount.
What is an ROI example?
Here’s a quick ROI example: If a company spends $1,000 on a CRM and earns $11,000 in new profits because of increased sales and better customer relationships thanks to the CRM in the first year, the ROI would be 1,000%, or 10x, for the first year.









